What is Access Control?
Access control refers to the processes, policies, and technologies that determine who is allowed to access specific data, systems, or resources, and under what conditions. It is a foundational element of cybersecurity and data governance, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information or perform specific actions within an enterprise environment.
Access control is not just about locking data away; it’s about granting the right access to the right people at the right time, while maintaining the security of everything else. From cloud platforms to on-premise servers, mobile devices to enterprise databases, modern access control systems must adapt to decentralized, hybrid, and highly dynamic ecosystems.
Types of Access Control
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Access permissions are assigned based on a user’s role within the organization.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Access decisions are made based on attributes like time, location, device, or security clearance.
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): Resource owners determine access permissions for users or groups.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Access is enforced by system-wide policies, typically in government or military settings.
Access Control as a Strategic Lever in the AI and Compliance Era
In 2025, access control is no longer just a security protocol—it’s a reflection of enterprise integrity, digital maturity, and operational resilience. As AI becomes more embedded in decision-making and regulatory frameworks grow increasingly complex, organizations must demonstrate not just that data is protected, but that access is justified, explainable, and traceable.
Modern access control plays a defining role in executing Zero Trust strategies, enforcing data localization mandates, and sustaining cross-border digital operations. It’s how enterprises prevent unauthorized inference in AI models, how they prove compliance during audits, and how they maintain customer trust in a hyper-connected ecosystem. The question is no longer “who has access,” but “who should have access—right now—and why?”
Access control, therefore, becomes a linchpin for secure innovation—empowering personalized experiences, secure collaboration, and real-time responsiveness without compromising data ethics or compliance.
Access Control Headwinds in 2025 – and How to Solve Them
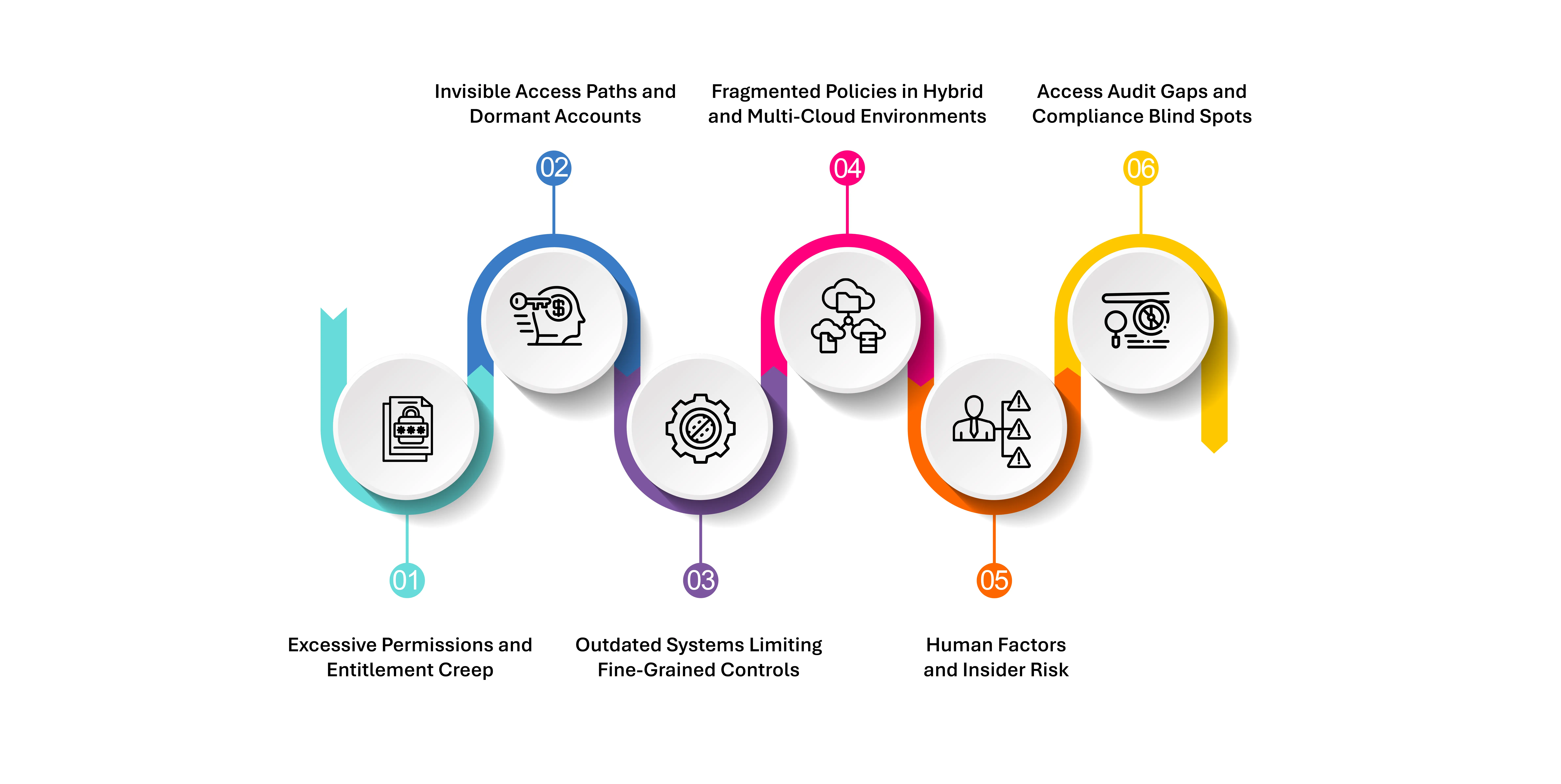
Excessive Permissions and Entitlement Creep
In large enterprises, access tends to accumulate over time. Employees retain permissions they no longer need due to role changes, internal mobility, or oversight. This creates hidden attack surfaces, especially when overprivileged accounts are compromised.
What to do: Implement continuous access certification campaigns, leverage policy-based provisioning linked to HR or business workflows, and integrate automated deprovisioning mechanisms to enforce least-privilege access dynamically.
Invisible Access Paths and Dormant Accounts
Shadow IT, orphaned service accounts, and forgotten test credentials can expose critical systems to exploitation. These invisible paths are often missed in routine audits but are highly attractive to threat actors for lateral movement or privilege escalation.
What to do: Deploy AI-powered identity threat detection and forensic access analysis to uncover and disable unused or misconfigured accounts. Pair this with lifecycle hooks to ensure every identity has a business owner, defined purpose, and expiration policy.
Outdated Systems Limiting Fine-Grained Controls
Many legacy applications don’t support modern access models, relying instead on static role hierarchies or hardcoded permissions. This makes it nearly impossible to enforce Zero Trust or accommodate modern compliance requirements.
What to do: Extend access granularity by wrapping legacy systems with API gateways or identity orchestration layers that enforce ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control) or dynamic RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) logic externally, without needing a full system overhaul.
Fragmented Policies in Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
With data and workloads spanning on-prem, private cloud, SaaS, and IaaS providers, enforcing uniform access policies becomes a governance nightmare. Inconsistencies increase exposure and reduce auditability.
What to do: Consolidate identity across platforms with federated SSO, and manage policies through a centralized policy-as-code engine. This ensures consistent enforcement of access controls across environments, regardless of infrastructure diversity.
Human Factors and Insider Risk
Not all threats come from outsiders. Excessive access, combined with a lack of oversight, increases the potential for unintentional misuse or malicious insider activity, particularly among privileged users or contractors.
What to do: Combine just-in-time access provisioning with behavioral analytics and continuous risk scoring to flag anomalies. Enable time-bound, context-sensitive access based on workflows and real-time trust levels, reducing standing privileges.
Access Audit Gaps and Compliance Blind Spots
In industries with strict compliance mandates (e.g., finance, healthcare, critical infrastructure), inability to trace who accessed what data, when, and why is a red flag. Many enterprises struggle with inconsistent or missing logs across systems.
What to do: Ensure every access event—especially to sensitive or regulated data—is logged with rich metadata including user identity, intent, device, location, and data sensitivity. Feed these logs into real-time SIEM systems and maintain immutable audit trails to support investigations and regulatory audits.
The Future of Access Control: Adaptive, Autonomous, and Mission-Critical
As enterprises embrace distributed architectures, sovereign AI models, and real-time data flows, access control is evolving from static enforcement to dynamic orchestration. Future-ready systems will embed intelligence directly into access decisions, adjusting privileges based on behavioral patterns, contextual risk, and business criticality in real time.
Expect access control to become autonomous and continuous, powered by machine learning, real-time observability, and privacy-by-design frameworks. These systems won’t just authorize access—they’ll justify it, monitor it, and revoke it autonomously when trust thresholds are breached.
Ultimately, access control is transforming into a strategic enabler of digital trust and operational agility. It’s how organizations will ensure ethical AI usage, comply with evolving sovereignty laws, and deliver secure, personalized services at scale, without ever losing control.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest Use Case: Privacy in Action: Automating Subject Access Requests with Zubin






