What is Retention Compliance?
Retention compliance refers to the adherence to legal, regulatory, and organizational policies governing how long data must be retained—and when it must be deleted. It ensures that enterprises store data only for as long as it’s legally required or operationally necessary, then dispose of it in a secure, auditable manner.
Whether it’s financial records, customer communications, health data, or employee information, different data types carry specific retention timelines dictated by global regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and the DPDP Act in India. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, legal exposure, and reputational damage.
Why Retention Compliance Matters
In today’s complex data landscape, compliance is no longer just about having the right data—it’s about retaining the right data for the right amount of time. Over-retaining data increases storage costs, security risk, and liability in the event of a breach. Under-retaining data can lead to failed audits, legal noncompliance, and regulatory penalties.
According to Deloitte, regulatory scrutiny around data retention is intensifying as global privacy laws mature. Retention compliance sits at the intersection of privacy, governance, and cybersecurity, playing a critical role in how enterprises manage data lifecycle, risk, and trust.
Key Elements of Retention Compliance
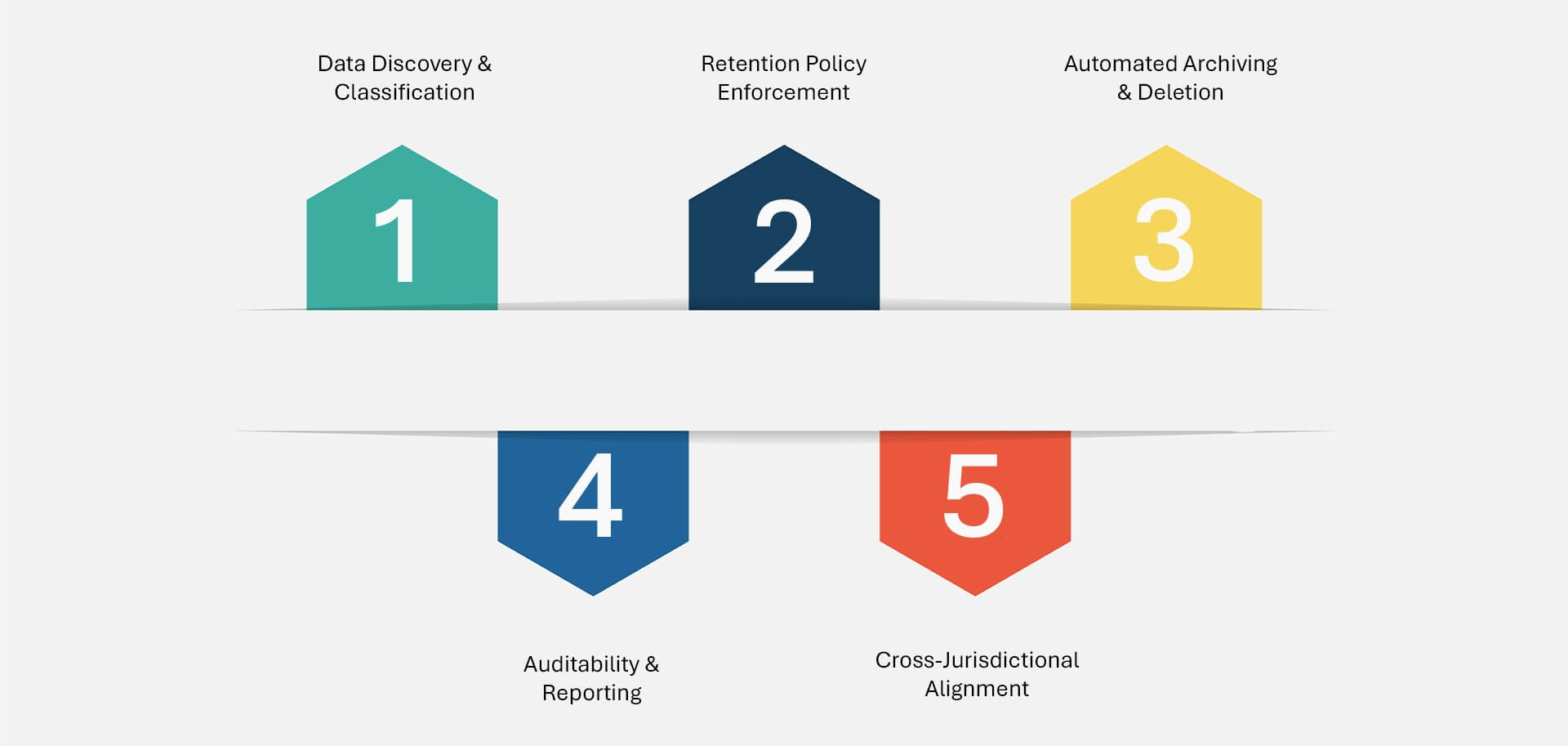
- Data Discovery & Classification: Identifying what data exists, where it resides, and how it’s categorized by regulatory or business value.
- Retention Policy Enforcement: Applying rules that define how long data should be retained, based on its type, origin, and applicable jurisdiction.
- Automated Archiving & Deletion: Moving data into compliant archival systems or securely deleting it when its retention period expires.
- Auditability & Reporting: Providing detailed logs, timestamps, and proof of compliance to auditors, regulators, and internal stakeholders.
- Cross-Jurisdictional Alignment: Ensuring global compliance by applying region-specific rules across hybrid environments.
Challenges in Retention Compliance – And How to Solve Them
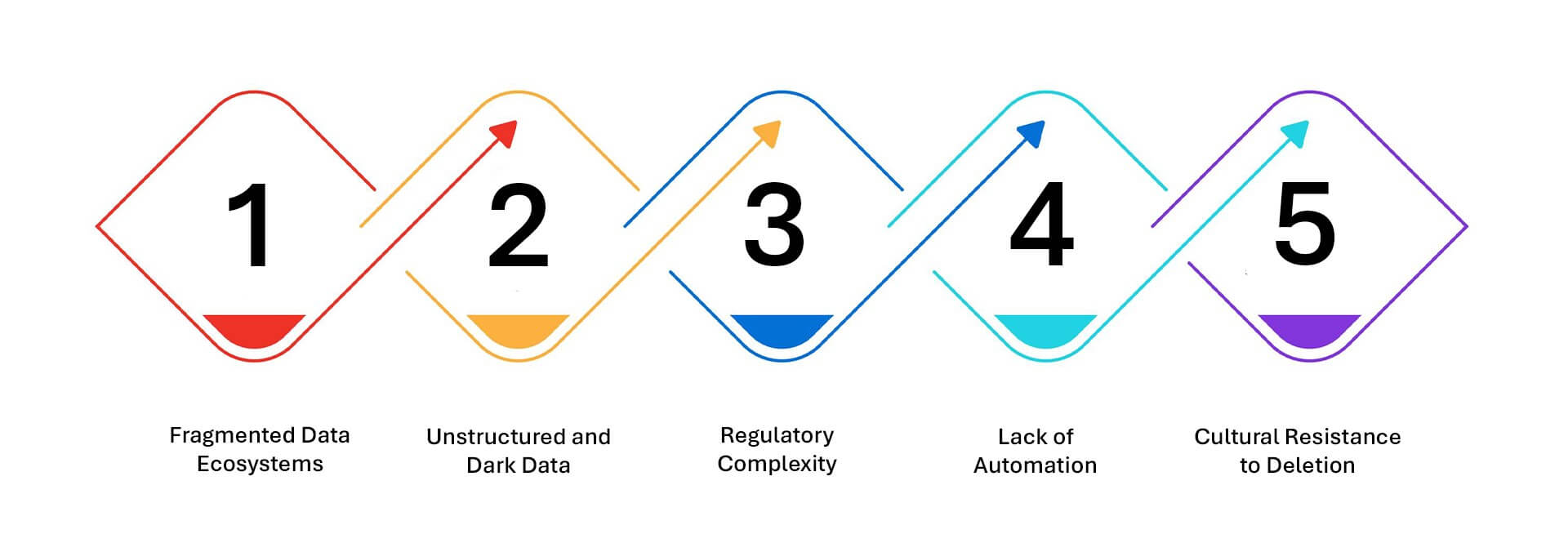
1. Fragmented Data Ecosystems
The Challenge:
Enterprise data is spread across multiple platforms—on-premises servers, cloud environments, email archives, collaboration tools, and third-party systems. This sprawl makes it difficult to apply consistent retention policies across the board.
The Solution:
Implement a unified data governance layer that connects to all major repositories through APIs or agentless discovery tools. This enables centralized policy enforcement while maintaining visibility across diverse environments. Metadata normalization and federated policy engines ensure compliance rules are applied consistently, regardless of where the data lives.
2. Unstructured and Dark Data
The Challenge:
The majority of enterprise data is unstructured, ranging from documents and emails to PDFs and multimedia files. Much of it is “dark,” meaning it’s unknown, unclassified, and unmanaged, increasing the risk of retaining regulated or sensitive data beyond its legal lifespan.
The Solution:
Use AI/ML-powered data discovery and classification tools that can scan, tag, and contextualize unstructured data. These tools can identify file types, extract key metadata (such as last accessed or owner), detect sensitive content (like PII or financial info), and apply appropriate retention or deletion policies based on content and risk level.
3. Regulatory Complexity
The Challenge:
Retention requirements vary widely—seven years for financial records in some regions, three years for employee data elsewhere, and permanent retention for specific legal records. Managing these nuanced, multi-jurisdictional requirements manually is inefficient and error-prone.
The Solution:
Deploy a compliance rules engine with built-in regulatory mappings by industry and geography. These engines can dynamically update based on changing legal mandates and automatically apply the correct retention schedule to each data class. Integration with legal and compliance teams ensures ongoing alignment with evolving laws like GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and DPDP.
4. Lack of Automation
The Challenge:
Manual processes—such as email-based reviews, spreadsheet tracking, and ad hoc deletion—are not scalable. They’re slow, prone to human error, and offer little transparency during audits or regulatory reviews.
The Solution:
Adopt policy-based automation tools that execute actions like archival, deletion, or alerts without manual intervention. These tools can be triggered by predefined metadata (e.g., date created, file type, sensitivity), and audit logs can be generated for each action. Workflow automation ensures retention policies are enforced consistently across systems in real time.
5. Cultural Resistance to Deletion
The Challenge:
Organizations often retain everything “just in case,” fearing that deleted data may one day be needed for legal, compliance, or business purposes. This leads to data hoarding, increased costs, and exposure in case of litigation or breach.
The Solution:
Introduce defensible deletion policies supported by legal hold workflows, retention justification audits, and user training. Pair this with dashboards and visualizations that show the cost, risk, and redundancy of over-retained data. Clear communication of the legal and financial implications of non-compliance helps shift mindsets from data hoarding to responsible data hygiene.
Rethinking Retention: A Strategic Lever for Risk Reduction, Data Privacy, and Sustainable Governance
Retention compliance has evolved far beyond traditional records management. In today’s enterprise, it’s a critical pillar of operational risk management, privacy protection, and ESG alignment. As the regulatory landscape grows more stringent and cyber threats become more pervasive, the mandate is clear: organizations must govern not just how they collect data, but how long they retain it, and when they securely dispose of it.
At the core of this shift is data minimization—a principle enshrined in modern regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and the DPDP Act. The more data you retain beyond its lawful or useful life, the greater your exposure in the event of a breach, litigation, or regulatory inquiry. Retention compliance ensures that sensitive or outdated data doesn’t become a silent liability lurking in your infrastructure.
But the benefits don’t stop at compliance or security. Retention compliance also plays a growing role in advancing environmental and sustainability goals. Every terabyte of unnecessary data consumes power, drives up storage costs, and expands an enterprise’s digital carbon footprint. By applying intelligent, policy-driven retention schedules and automating defensible deletion, enterprises reduce data center load, optimize resource utilization, and demonstrate a tangible commitment to ESG reporting standards.
Forward-looking organizations are implementing AI-powered retention engines that dynamically classify data, apply jurisdiction-specific policies, and trigger lifecycle actions across hybrid environments. These systems not only reduce manual effort and error but also ensure every piece of data is retained for the right duration, and no longer.
Ultimately, retention compliance is about control: control over data risk, control over regulatory outcomes, and control over your environmental impact. In an era where data is both a strategic asset and a potential liability, knowing when to say “enough” is a mark of digital maturity.
Because when it comes to compliance, timing isn’t just everything—it’s your defense.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest blog: Data Sovereignty Is No Longer a Policy Debate. It’s the New Rulebook for Digital Governance






