What Is an Unstructured Data Engine?
An Unstructured Data Engine is a specialized software or architectural framework designed to ingest, analyze, classify, govern, and act upon unstructured data—such as emails, PDFs, videos, sensor logs, audio files, and images—across complex IT environments.
Unlike traditional structured data platforms that rely on rigid schemas (e.g., rows and columns in a database), unstructured data engines are built to handle heterogeneous, high-volume, context-rich datasets that lack predefined formats. They often integrate AI/ML capabilities, metadata analysis, and policy enforcement to extract business value and reduce risk from unstructured information.
Why It Matters
In 2025, unstructured data accounts for over 80–90% of enterprise data, yet remains largely invisible, underutilized, and ungoverned. This creates blind spots not only in operational efficiency, but also in AI readiness, regulatory compliance, and cybersecurity posture.
An Unstructured Data Engine serves as the control plane for these high-risk, high-value datasets, providing the intelligence and automation needed to convert dark data into a strategic asset.
Strategic Functions of an Unstructured Data Engine
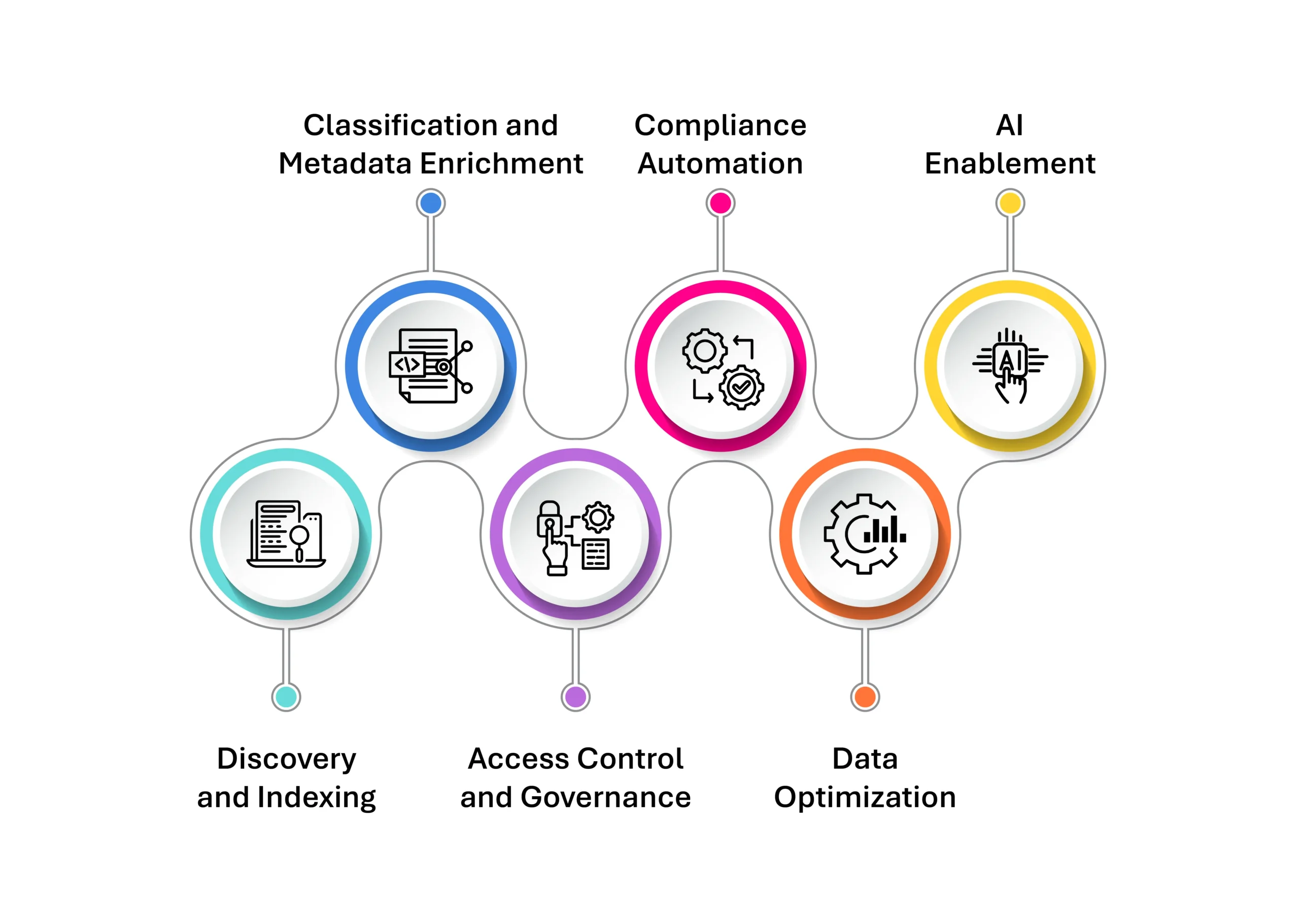
- Discovery and Indexing: Scans distributed environments to locate, inventory, and index all forms of unstructured data.
- Classification and Metadata Enrichment: Uses rules or AI/ML to tag sensitive content (e.g., PII, PHI, financial data) and derive contextual insights through metadata analysis.
- Access Control and Governance: Integrates with role-based access models, enabling secure data sharing and remediation of permission sprawl.
- Compliance Automation: Supports regulatory obligations like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, or DPDP by identifying sensitive records and triggering retention, masking, or deletion workflows.
- Data Optimization: Assesses data usage patterns to reduce ROT (Redundant, Obsolete, Trivial) data, improve storage efficiency, and cut cloud or infrastructure costs.
- AI Enablement: Prepares clean, contextualized, and compliant data for AI pipelines—ensuring model accuracy, traceability, and ethical integrity.
Key Challenges Solved by an Unstructured Data Engine – And How

1. Data Fragmentation Across Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Unstructured data is scattered across file shares, collaboration tools, legacy systems, cloud buckets, and edge devices, making it nearly impossible to manage holistically.
How the engine helps: An Unstructured Data Engine offers centralized discovery, indexing, and federation, enabling organizations to create a unified data inventory across all environments. It normalizes access to metadata and content, regardless of location or format, and provides a single governance layer to enforce policies enterprise-wide.
2. Lack of Visibility into Sensitive or Business-Critical Data
Enterprises struggle to locate or classify sensitive data such as PII, PHI, or IP, which can lead to compliance violations, legal exposure, or poor AI model performance.
How the engine helps: Through AI/ML-powered data classification and content analytics, the engine automatically detects and tags sensitive information. It enhances metadata with business context, enabling rapid search, classification, and downstream automation for compliance, governance, and remediation.
3. Regulatory Complexity and Non-Compliance Risk
Global regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and DPDP require organizations to prove where data resides, how it’s used, and when it must be deleted or masked.
How the engine helps: It embeds policy-based automation, enabling dynamic retention schedules, legal holds, and compliance workflows. The engine tracks lineage, access history, and data movement—providing full traceability and defensible audit trails for regulatory reporting and Subject Access Requests (SARs).
4. Poor Data Quality and AI Risk Exposure
AI models trained on outdated, redundant, or irrelevant data can produce biased or unreliable outcomes, undermining trust in predictions.
How the engine helps: The engine improves data readiness by identifying duplicate, obsolete, or low-quality datasets and suggesting actions like deduplication, enrichment, or deletion. This ensures that only clean, contextual, and compliant data feeds into AI pipelines, enhancing model accuracy, fairness, and auditability.
5. Inefficient Storage and Spiraling Cloud Costs
Unstructured data growth leads to bloated storage environments and uncontrolled cloud spend, with over 60% of stored files often being redundant or unused.
How the engine helps: Using intelligent data lifecycle management, the engine assesses usage patterns, aging, and business relevance. It automates the movement of cold or ROT (Redundant, Obsolete, Trivial) data to lower-cost storage tiers, archives, or deletion—optimizing both performance and cost.
6. Data Sovereignty and Residency Violations
In jurisdictions with strict localization laws, organizations risk penalties if regulated data is stored or accessed across borders.
How the engine helps: It enforces geo-fencing and jurisdiction-aware policies, ensuring sensitive data remains within defined borders. The engine monitors location, access, and replication, flagging or blocking violations in real time and supporting localized processing for compliance with national data laws.
7. Manual Governance and Scalability Limits
Relying on human intervention for classification, tagging, and permissions management doesn’t scale and invites human error.
How the engine helps: With automated workflows and intelligent recommendations, the engine accelerates governance actions at scale, such as access reviews, permissions cleanup, and reclassification. It enables self-service management for data owners, decentralizing control without losing compliance oversight.
The Future of the Unstructured Data Engine: Intelligent, Autonomous, Secure
The future of the Unstructured Data Engine lies in its evolution into an intelligent, autonomous, and secure backbone for enterprise data ecosystems. AI will enable these engines to go beyond basic discovery—automatically classifying, enriching, and acting on unstructured data in real time. By recognizing patterns, detecting risks, and triggering policy-based actions like masking, deletion, or retention, the engine will power smarter decisions and reduce manual intervention. As data becomes more decentralized, federated governance capabilities will ensure organizations can manage compliance, privacy, and sovereignty across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, without losing control.
Security will be embedded at the architecture level, with AI-driven anomaly detection, self-healing protocols, and zero-trust enforcement guarding sensitive assets. Meanwhile, real-time automation will handle privacy requests, regulatory updates, and audit trails proactively—turning compliance into a continuous, invisible process. In this new era, the Unstructured Data Engine won’t just support operations—it will differentiate enterprises by enabling ethical AI, resilient governance, and trusted innovation at scale.
The future of the Unstructured Data Engine is not just about speed and efficiency; it’s about enabling organizations to navigate complexity with agility, resilience, and trust. With AI-driven intelligence, autonomous governance, and security-by-design, the Unstructured Data Engine will become a central platform in transforming unstructured data from a risk into a strategic asset.
For organizations that embrace this evolution, it’s not just about staying compliant—it’s about transforming data management into a competitive advantage that drives innovation, operational efficiency, and customer trust in an increasingly complex and regulated digital landscape.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest blog: Sovereign AI and the Future of Nations: Why Data, Infrastructure, and Intelligence Must Align






