- The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a profound shift known as Industry 4.0, marked by the fusion of cutting-edge technologies with traditional production methods.
- The concepts of data interoperability and analytics are pivotal in unraveling the intricacies of data and facilitating seamless communication between systems, devices, and teams.
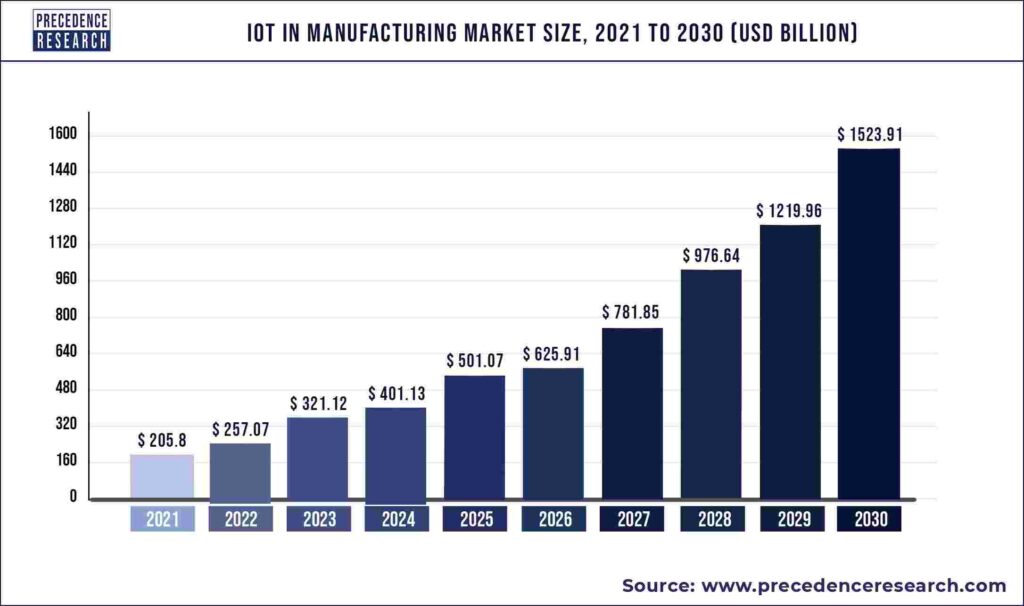
- Industry 4.0 is characterized by an inundation of data orchestrated by the proliferation of IoT devices, sensors, and interconnected systems. By 2025, IoT devices alone are projected to generate nearly 79.4 zettabytes of data annually in the manufacturing sector.
- The synergy of data interoperability and analytics yields a spectrum of benefits. Manufacturing efficiency skyrockets as machines and systems converse seamlessly, driving down operational costs.
- Navigating the labyrinth of unstructured data challenges calls for inventive approaches. Data Dynamics’ Unified Unstructured Data Management Platform shines as a beacon in this endeavor.
In the grand evolution of the world, where innovation paints a constantly shifting canvas, a chapter of transformation has left an indelible mark on manufacturing: Industry 4.0. This era is a symphony of cutting-edge technologies, where digital prowess converges with traditional production, creating a harmonious blend that resonates across factory floors worldwide. Industry 4.0’s impact on manufacturing transcends the boundaries of automation; it’s a paradigm shift that orchestrates the very essence of how products are conceptualized, created, and delivered. At its core lies the mesmerizing dance of data – an invisible thread weaving through every process and operation, driving the machinery of modern production to newfound heights.
In this unfolding transition, data interoperability and data analytics emerge as the magicians wielding spells of efficiency and insight. In the data-driven core of Industry 4.0, these concepts enchant the manufacturing realm with their promise to untangle the web of information, allowing systems, machines, and teams to communicate effortlessly. Data interoperability, akin to a universal language spoken across digital landscapes, harmonizes the symphony of diverse devices, while analytics, the translator of raw data into actionable wisdom, empowers decision-makers to wield foresight in their strategic moves. This amalgamation casts a spell of transformation, turning mundane data into the gold of informed decisions, guiding manufacturers toward precision and competitiveness.
The Data Deluge in Manufacturing
Stepping onto a modern manufacturing floor – it’s like entering a vibrant digital world. Here, machines and humans collaborate seamlessly, orchestrating operations with an incredible efficiency. The reason behind this transformation? Data, and lots of it. By 2025, the global manufacturing industry is expected to churn out a mind-boggling 44 trillion gigabytes of data each year. But it’s not just about the sheer volume of data; it’s about how it’s generated. Inside these smart factories, data creation is non-stop. A regular smart factory can produce more than 5 petabytes (PB) of data every single week. To put that into perspective, it’s equivalent to all the data stored in over a million laptops. This torrent of data comes from everywhere – sensors, devices, and corners you wouldn’t even think of. It’s like a constant flow of digital information, bringing the factory to life in ways we’ve never seen before.
Today machines have a voice, products tell stories through their manufacturing journey, and production lines hum with digital vitality. This reality brought to life by the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, and interconnected systems form the backbone of Industry 4.0. From temperature sensors gauging the perfect conditions for a chemical reaction to RFID tags tracking products on their voyage through the assembly line, data is generated at a breathtaking pace, creating an intricate web of insights that promise to redefine the manufacturing landscape. In the manufacturing sector alone, it’s projected that by 2025, IoT devices will generate approximately 79.4 zettabytes of data annually. To put this in perspective, one zettabyte is equivalent to a billion terabytes – an astronomical amount of information coursing through the digital veins of production facilities. Every machine vibration, every temperature fluctuation, and every component movement adds to this torrent of data, forming the building blocks of the smart factories of tomorrow.
Yet, beneath this sea of data lies a challenge that demands attention: diversity. The data generated in manufacturing processes is far from uniform. It comes in a myriad of formats – structured and unstructured, numerical and textual – creating a puzzle of information that needs to be pieced together. Additionally, data doesn’t adhere to the boundaries of a single platform. Legacy systems, modern machinery, and cutting-edge software may each speak a different language, posing a significant hurdle in harnessing the true potential of this data torrent.
This is where the concept of data interoperability steps onto the stage, offering a bridge to unify disparate data sources, formats, and platforms and transforming the cacophony into a symphony that manufacturers can conduct with precision.
What is Data Interoperability?
In the manufacturing sector’s journey towards Industry 4.0, data interoperability is the linchpin that connects the dots. It’s the ability of various systems, irrespective of origin, to communicate seamlessly and share data in a universally understood language, creating a scenario where a sensor in the machining center converses fluently with the inventory management software, relaying real-time production updates and material usage. Take communication protocols for instance. As we are all aware, different machines speak different languages – leading to a maze of diverse information that hampers communication and understanding. In manufacturing, this often manifests as a myriad of protocols, software systems, and data formats. This is where standardized communication protocols step in as the translators, facilitating a coherent dialogue among diverse entities. Protocols like OPC UA (Unified Architecture) and MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) enable machines and systems to converse in a harmonious symphony of data. This standardization isn’t just a convenience; it’s the cornerstone of efficient data exchange that paves the way for increased agility, productivity, and insight. Data interoperability breathes life into this exchange, transforming manufacturing floors into interconnected ecosystems where efficiency and collaboration reign.
Here are five manufacturing companies that have embraced data interoperability to enhance their production efficiency:
- Siemens AG: A global powerhouse in the manufacturing and energy sectors, Siemens is a prime example of a company that has harnessed data interoperability to optimize its processes. Siemens leverages the OPC UA standard for seamless communication between various components of their industrial automation systems. This has allowed them to achieve better coordination between production lines, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
- General Electric (GE): GE’s journey into the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has been marked by its use of data interoperability. GE has connected its machines and devices across different facilities by implementing the Predix platform, which supports open standards like OPC UA. This interconnectedness has enabled predictive maintenance, streamlined supply chains, and improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
- Bosch: As a leading global supplier of technology and services, Bosch has embraced data interoperability to enhance its manufacturing processes. The company employs standardized communication protocols to connect its diverse range of products and systems. By doing so, Bosch has achieved better synchronization in its production lines, reducing cycle times and improving resource utilization.
- Procter & Gamble (P&G): P&G, a consumer goods giant, has leveraged data interoperability to optimize its supply chain and manufacturing operations. By integrating data from various sources, including suppliers and production facilities, P&G can forecast demand more accurately, ensuring timely replenishment of raw materials. This approach has led to reduced inventory costs and enhanced production efficiency.
- Ford Motor Company: Ford has embraced data interoperability to create a more connected and efficient manufacturing ecosystem. By adopting IoT technologies and standardized communication protocols, Ford can monitor and control various aspects of its manufacturing processes in real-time. This has resulted in improved quality control, reduced waste, and enhanced overall operational efficiency.
These examples highlight how data interoperability isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s a practical strategy that manufacturing giants are using to streamline their operations, improve collaboration, and gain a competitive edge in the Industry 4.0 landscape. Speaking of gaining an edge…
Revolutionizing Decision-Making with Analytics
In the world of manufacturing, making smart decisions isn’t a matter of luck – it’s a matter of gaining ultimate insights from your data to make informed decisions. Data analytics transforms raw manufacturing data into valuable insights that guide operations and strategies. It’s like turning a puzzle of numbers into a clear picture of what’s happening and what’s possible. Let’s break down the roles of analytics in manufacturing, backed by real-world examples and statistics.
- Descriptive Analytics: Think of descriptive analyticsas a snapshot of the present. It looks at historical data to show exactly how things are going right now. Manufacturers can see the big picture, track performance metrics, and spot any bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
- General Electric utilizes data analytics to monitor gas turbines’ performance in real time. By analyzing data from thousands of sensors, they optimize turbine efficiency, reducing downtime and operational costs.
- Toyota utilizes descriptive analytics to monitor its assembly lines, analyzing data to detect deviations from expected production patterns. This allows them to make immediate adjustments and ensure consistent quality.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics takes a step into the future. By analyzing historical data alongside real-time data, it can forecast what might happen next. For manufacturers, this means being able to predict equipment failures or production slowdowns before they even occur. According to a study by Deloitte, predictive analytics in manufacturing reduces maintenance costs by up to 25% and unplanned downtime by 50%.
- Bosch uses predictive analytics to predict and prevent machine failures in its automotive manufacturing plants.
- Volkswagen use predictive analytics to forecast supply chain disruptions, allowing them to adjust production plans and maintain a smooth flow of operations.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predictions – it tells you what actions to take. It recommends the best course of action to achieve specific goals by considering various factors and possibilities. Manufacturers can optimize production workflows, allocate resources effectively, and make decisions based on data-backed recommendations.
- BMW uses prescriptive analytics to adjust production schedules in real time, considering factors like demand fluctuations and supply chain disruptions.
- Airbus employs prescriptive analytics to optimize aircraft assembly. By analyzing data from various stages of assembly, they can recommend adjustments to minimize production bottlenecks and enhance quality.
By infusing analytics at each of these stages, manufacturers gain the capability not just to respond to situations, but to actively mold their operations for better efficiency. Teams become increasingly data-oriented, utilizing insights to fine-tune procedures and implement gradual improvements, allowing them to not merely react to circumstances but to preempt them and shape their operations for efficiency and success. This transition towards data-supported decision-making fundamentally reshapes the manufacturing landscape, ensuring smoother workflows, diminished expenditures, and heightened competitiveness. It ushers in a dynamic arena where technology and data converge harmoniously.
The Seven-Point Advantage of Data Interoperability and Analytics in Industry 4.0
In the realm of modern manufacturing, data isn’t just ones and zeros – it’s the secret ingredient that transforms operations, enriches decision-making, and fuels innovation. Data interoperability and analytics join forces as the dynamic duo that amplify every facet of the manufacturing lifecycle, revolutionizing processes from design and production to supply chain management and sustainability efforts. This paradigm shift is not only driving efficiency gains but also cultivating a new standard of precision and impact, reshaping industries and setting new benchmarks for success. Let’s delve into the core phases of this transformation.
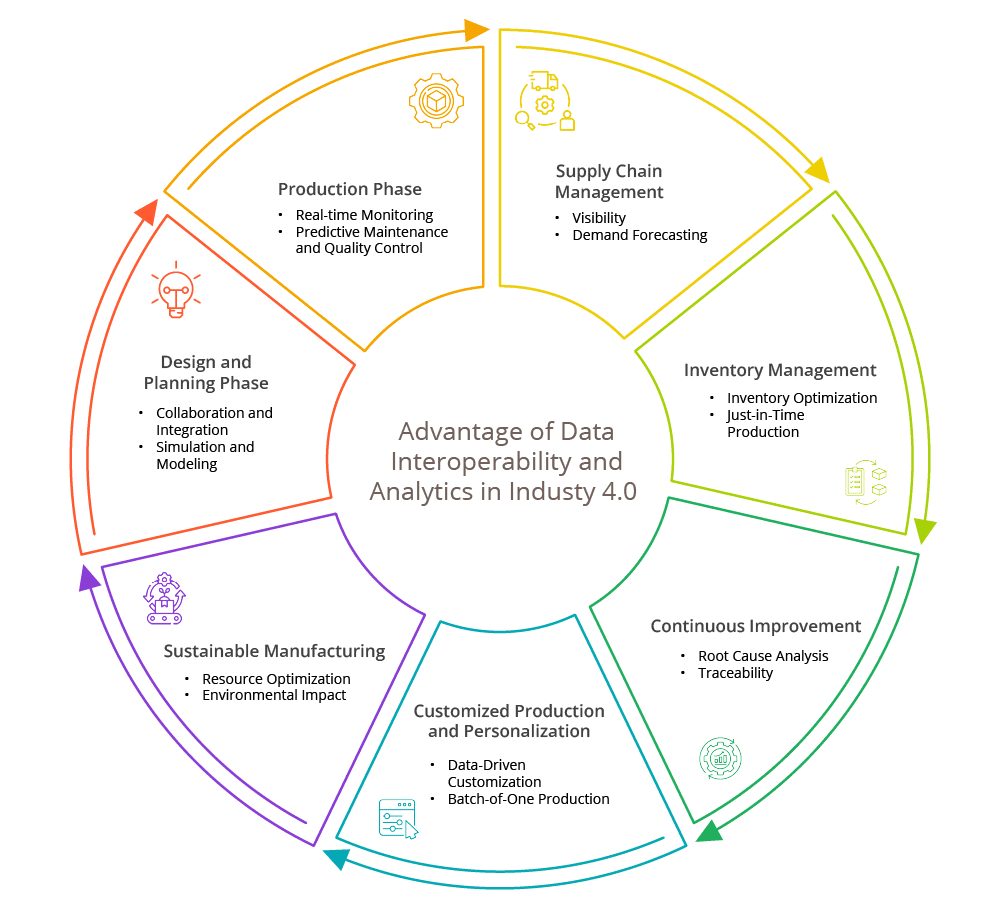
1. Design and Planning Phase:
- Collaboration and Integration: Through seamless data interoperability, cross-disciplinary teams of engineers and designers collaborate effectively, yielding precise product design and process planning. Deloitte’s study reveals a 3.6% higher gross margin for interoperability advocates. Airbus’ digital tools slashed time-to-market by half, as design and production teams harmonized efforts.
- Simulation and Modeling: Data analytics emulate scenarios with historical data, optimizing production processes and resource allocation before execution. Volkswagen’s Autoeuropa plant reaped a 10% productivity boost via layout optimization.
2. Production Phase:
- Real-time Monitoring: By harnessing live data from interconnected devices, analytics oversee operations, detect anomalies, and uphold production continuity. Capgemini underlines real-time monitoring as the paramount benefit of Industry 4.0, resonating with 56% of manufacturers.
- Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control: Data-driven prognostication averts equipment downtime and identifies quality deviations, trimming costs. Deloitte emphasizes predictive maintenance’s potential for 20% higher asset utilization and 5-10% reduced maintenance expenses.
3. Supply Chain Management:
- Visibility: Data interchange among stakeholders amplifies supply chain coordination, demand foresight, and inventory control. McKinsey underscores 10-30% lower inventory costs via augmented supply chain visibility. Amazon’s real-time data liaison with suppliers bolsters inventory efficiency and swift customer deliveries.
- Demand Forecasting: Analytics leverage historical and real-time data, predicting demand shifts for agile production scheduling and optimized inventory. Procter & Gamble’s predictive prowess carved $1 billion off inventory costs while heightening service quality.
4. Inventory Management:
- Inventory Optimization: Data analytics optimize stock levels, curbing overages and shortages for cost savings. Lufthansa Technik’s data-based strategy trimmed inventory by 20% while upholding 98% availability.
- Just-in-Time Production: Real-time inventory insights empower lean just-in-time production. Fast Retailing’s real-time analytics-driven approach syncs inventory with demand, minimizing excess stock.
5. Continuous Improvement:
- Root Cause Analysis: Data analytics illuminate inefficiencies, driving ongoing enhancements. General Electric’s data-driven insights induced a 10% productivity surge and defect reduction.
- Traceability: Uninterrupted data traceability from components to end products bolsters safety and curtails recalls. Dassault Systèmes asserts 70% support for traceability. GlaxoSmithKline’s ingredient tracking ensures product quality and authenticity.
6. Customized Production and Personalization:
- Data-Driven Customization: Interoperability and analytics personalize production based on customer preferences, upscaling satisfaction. Nike’s data-fueled customization led to a 300% uptick in online sales.
- Batch-of-One Production: Agile factories pivot toward tailored, cost-effective small-batch or individual unit production. McKinsey cites 40% lead time reduction and 20% machine utilization rise. Adidas’ Speedfactory slashed lead times by two-thirds through data-driven flexibility.
7. Sustainable Manufacturing:
- Resource Optimization: Data analytics optimize resource usage, aligning with sustainability targets. World Economic Forum predicts 10-15% energy cut via data-driven resource optimization. BMW’s smart factories decreased water usage by 45% and energy consumption by 30%.
- Environmental Impact: Interoperability records emissions and waste data, enabling ecological decisions. Data-driven optimization curtails energy consumption and emissions by 5-15%. Volvo Trucks’ analytics-driven engine tweaks cut CO2 emissions by a fifth.
Unstructured Data: The Biggest Challenge in Achieving Interoperability and Analytics
While the possibilities of data interoperability and analytics in the manufacturing sector are enticing, a formidable challenge looms in the shadows – unstructured data. As we explore the realm of Industry 4.0, this challenge surfaces as a complex puzzle that demands innovative solutions. Unstructured data, comprising diverse formats like text, images, and videos, makes up for 80% of enterprise data and introduces a layer of complexity that must be addressed to realize the potential of data-driven operations fully.
Unstructured data, unlike neatly organized, structured data, exists in various formats without a predefined structure. It’s the scribbled notes in maintenance logs, the images captured by sensors, and the sounds of machinery captured as audio. While this data harbors a wealth of insights, its lack of uniformity presents a challenge. Data interoperability thrives on standardized communication protocols. However, unstructured data doesn’t conform to these standards as easily. Imagine trying to fit the fluidity of human communication into a rigid framework. This is the hurdle that unstructured data poses. Integrating such data into the realm of interoperability requires inventive methods.
Unstructured data doesn’t just challenge interoperability; it also tests the capabilities of analytics. Drawing insights from text, images, and audio demands advanced algorithms capable of understanding context and sentiment. Unlike structured data that can be fed directly into analytical models, unstructured data requires preprocessing and transformation to make it compatible. This additional layer of complexity underscores the necessity for innovative approaches to analytics. But there’s a solution to untangle this mess – Unified Data Management.
The Data Dynamics Advantage
Data Dynamics emerges as a trailblazing provider of enterprise data management solutions in this groundbreaking arena. At the forefront of this revolution is their Unified Unstructured Data Management Platform – a game-changing tool that empowers organizations to harness the latent power of unstructured data. This visionary platform is a composite of four key modules: Data Analytics, Mobility, Security, and Compliance. Its success has already been demonstrated across a spectrum of over 300 organizations, including 28 Fortune 100 and 5 Fortune 500 manufacturing giants.
Data Dynamics’ platform emerges as the definitive all-in-one solution, arming manufacturers with the tools they need to capitalize fully on unstructured data’s potential. The platform’s prowess lies in its ability to usher in technologies like Data Interoperability, allowing organizations to seamlessly categorize, tag, index, analyze, archive, and migrate data across diverse sources. This transformation bestows structure upon raw data, elevating it from mere storage to the realm of invaluable business assets.
Here are five ways how the Data Dynamics Unified Data Management Platform aids data interoperability and analytics:
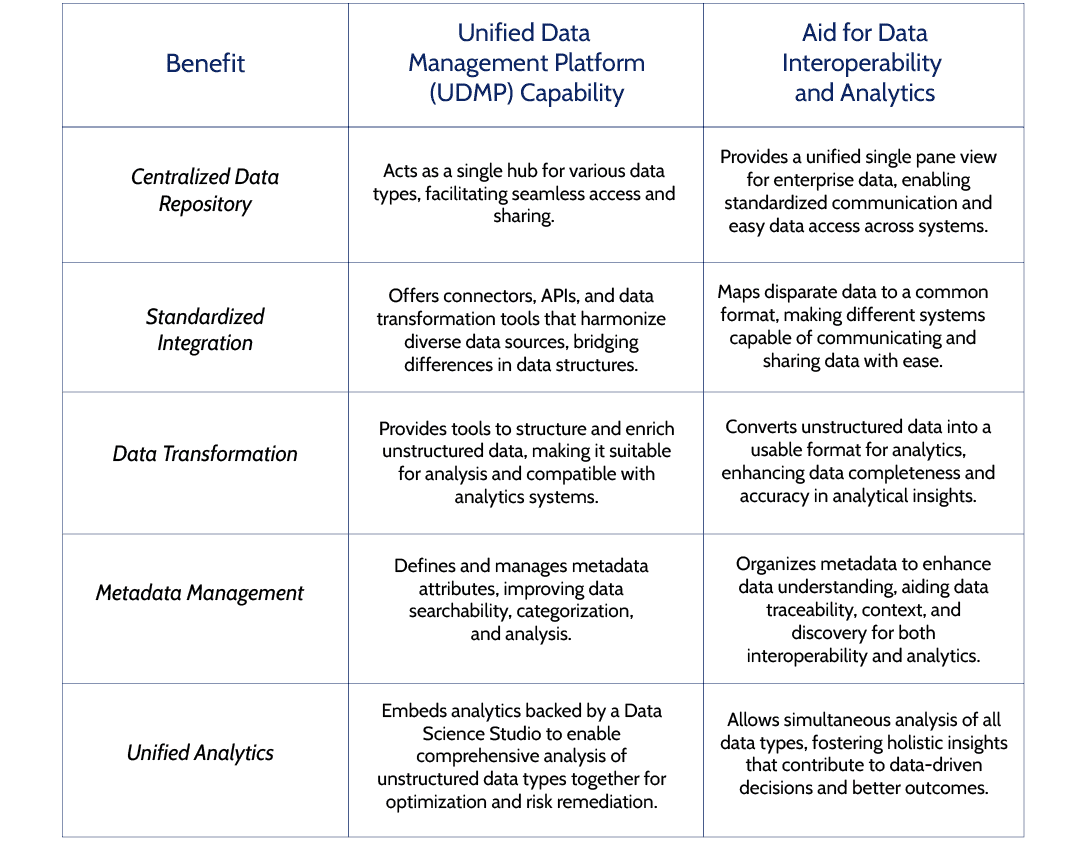
With the Data Dynamics platform, manufacturers are empowered to discern the most pertinent data types and chart out strategies for its storage – a process that curbs data sprawl, centralizes data repositories, and optimizes storage efficiency.
To delve deeper into the world of possibilities that Data Dynamics can unlock for your enterprise and to ensure your business remains at the forefront of progress, visit www.datadynamicsinc.comor reach out to us at solutions@datdyn.com | (713)-491-4298.






