In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity has become a paramount concern for industries across the board when it comes to their data privacy. The manufacturing sector, in particular, faces unique challenges and vulnerabilities in safeguarding its valuable data. As manufacturing processes become increasingly digitized and reliant on technology, the need for robust cybersecurity measures is more critical than ever. This article explores the significance of cybersecurity in the manufacturing sector and provides an overview of the data storage challenges and vulnerabilities that manufacturers must address.
The Evolving Threats cape Targeting the Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector plays a pivotal role in the global economy, producing goods that touch nearly every aspect of our daily lives. From automotive and electronics to pharmaceuticals and aerospace, manufacturers handle vast amounts of sensitive data, including intellectual property, customer information, and supply chain details. As the sector becomes more interconnected and reliant on digital technologies, it becomes an attractive target for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain, industrial espionage, or even sabotage.
A successful cyber attack on a manufacturing company can have severe consequences. According to IBM, the average financial toll of a data breach in 2022 reached a staggering $4.35 million. However, the manufacturing industry endured even more astonishing costs, with an average of $4.47 million, exhibiting a 5.4% increase compared to the previous year.
Additionally, according to Statista 2022, manufacturing had the highest share of cyber attacks among the leading industries worldwide accounting for nearly 25 percent of the total cyber attacks.
Distribution of cyber attacks across worldwide industries in 2022
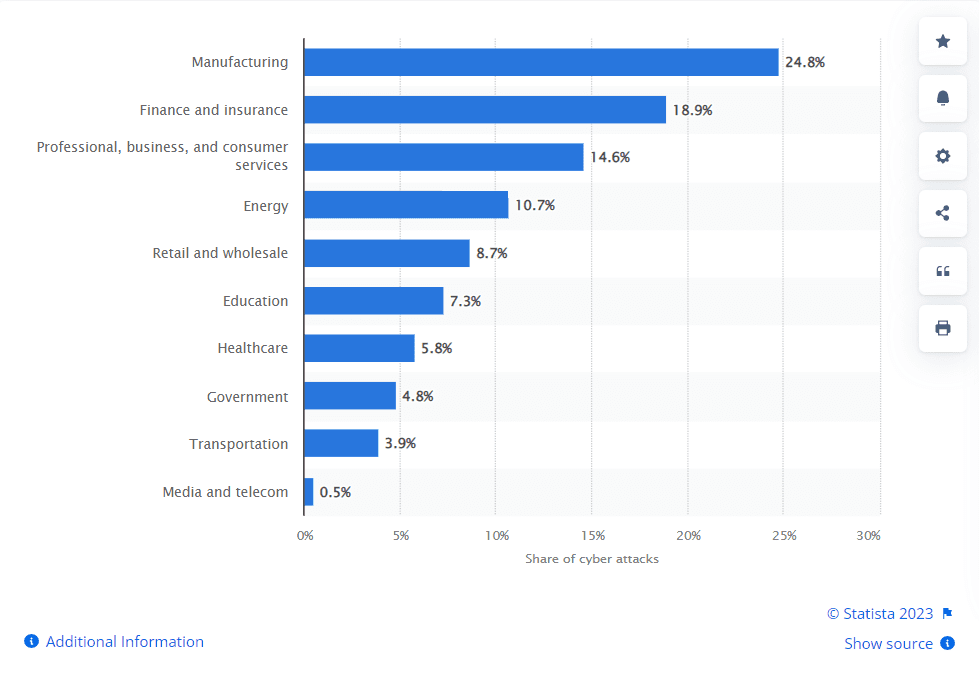
Manufacturing companies often endure substantial losses in their operations and revenue due to cyber attacks, which can bring about the temporary closure of one or more facilities while addressing the damages. Beyond these disruptions, such assaults can also result in the exposure of sensitive data and valuable intellectual property, leading to further financial harm. It can result in production disruptions, loss of proprietary information, compromised customer trust, financial damages, and potential safety risks. Also, if a competitor exploits this stolen data to develop and launch a competing product, it could lead to a significant loss of market share or even the downfall of the targeted manufacturer. Moreover, the interconnected nature of modern manufacturing ecosystems means that a cyber breach in one part of the supply chain can have far-reaching implications for the entire network, affecting multiple organizations and causing cascading disruptions.
Distribution of cyber incidents in manufacturing organizations worldwide from October 2021 to September 2022, by type
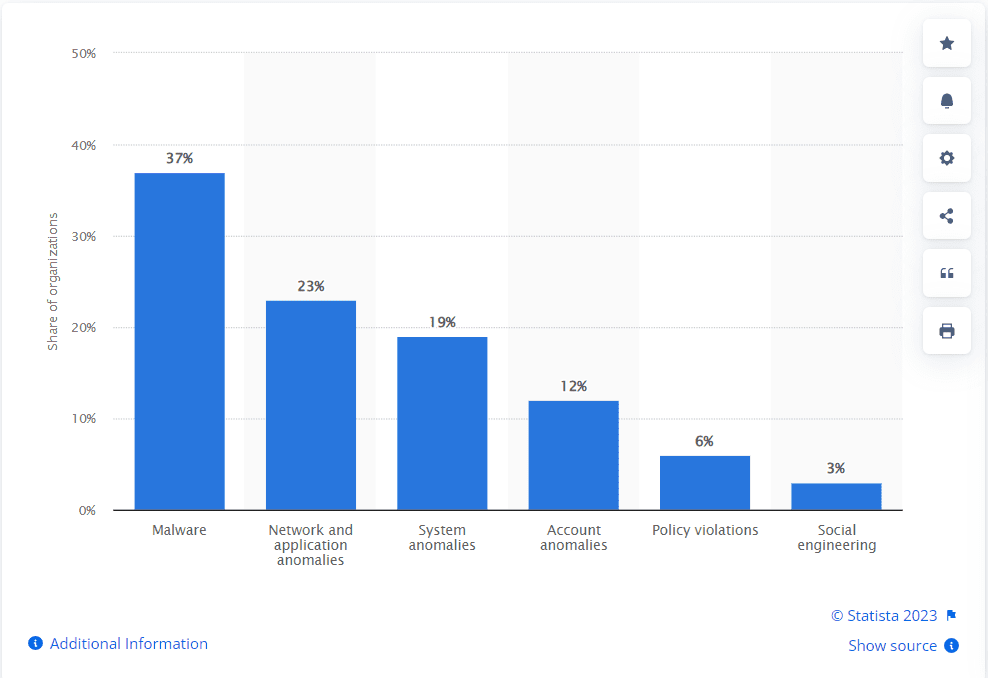
- Malware and Ransomware Attacks: Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, or ransomware, can infiltrate manufacturing systems, disrupt operations, encrypt critical data, and demand ransom for its release.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Cybercriminals often employ deceptive tactics, such as phishing emails or phone calls, to trick employees into divulging sensitive information or granting unauthorized access to systems.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with privileged access to manufacturing systems can intentionally or unintentionally cause security breaches, either through malicious intent or inadvertent actions.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: The complex nature of manufacturing supply chains presents opportunities for cybercriminals to infiltrate systems through vulnerable partners, suppliers, or third-party services.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Manufacturing companies invest significant resources in research and development, making them attractive targets for cyber espionage aimed at stealing proprietary information, trade secrets, or product designs.
- Operational Disruption: Cyber attacks targeting industrial control systems (ICS) can disrupt production processes, causing operational downtime, equipment failures, and financial losses.
To sum up, manufacturing organizations face an elevated risk of cyberattacks, particularly as they embrace digitization in the era known as Industry 4.0. But what is Industry 4.0 and how is it contributing to the increase of cyber-attacks in manufacturing? Let’s deep dive.
Industry 4.0. – A Boon or a Bane? 5 Challenges. 5 Resolutions
The manufacturing industry has witnessed an extraordinary evolution, propelling humanity on an exhilarating journey through the ages. From the birth of Industry 1.0, characterized by mechanization and steam power, to the dawn of Industry 4.0, where cyber-physical systems and the Internet of Things reign supreme, the transformation has been nothing short of awe-inspiring. Imagine stepping back in time, witnessing the clanking gears and billowing smoke of the early factories that kickstarted the Industrial Revolution. Fast-forward to Industry 2.0, with electrification powering assembly lines and unleashing unimaginable productivity. The advent of Industry 3.0, marked by computerization and automation, propelled manufacturing to new heights, with robots seamlessly working alongside their human counterparts. But the revolution did not stop there. Industry 4.0 emerged and embraced the fusion of physical and digital realms. Intelligent machines, interconnected systems, and big data analytics now form the beating heart of manufacturing, enabling factories to become smart, flexible, and hyper-efficient.
However, amidst the incredible advancements, a growing concern looms large: the vulnerability of Industry 4.0 to cybercrimes. As factories become more interconnected and reliant on digital systems, the risks associated with cyber threats have escalated significantly. Let’s delve into the reasons behind the susceptibility of Industry 4.0 to cybercrimes in manufacturing, shedding light on the challenges and offering insights into potential solutions.
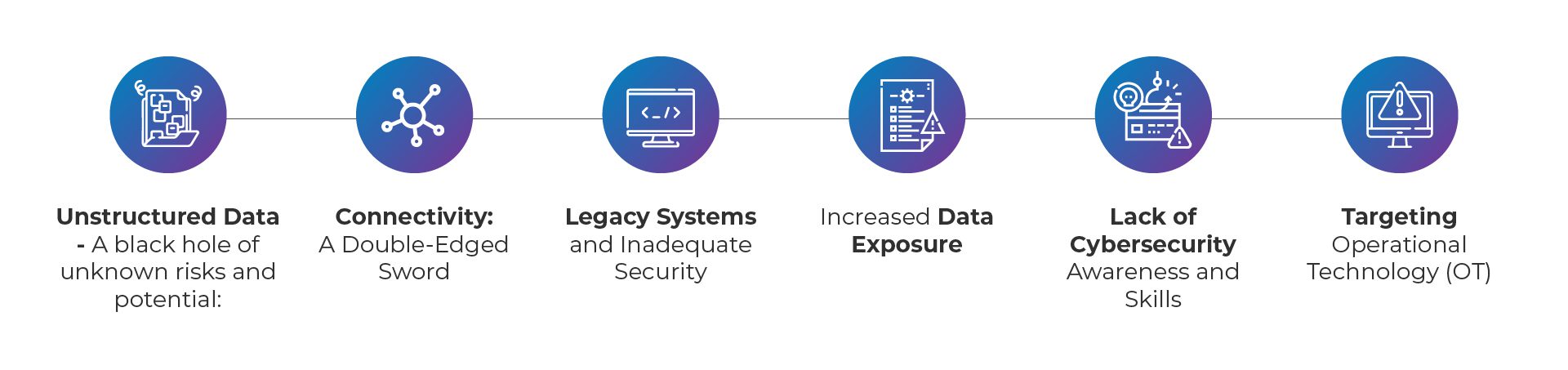
1. Unstructured Data – A black hole of unknown risks and potential:
In the dynamic realm of Industry 4.0, the manufacturing landscape has witnessed an unprecedented surge in unstructured data, ushering in a new era of possibilities and challenges. Within the smart factory premises, a myriad of machines, including industrial plants, production lines, air conditioning units, and indispensable uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, occupy the bustling floor. These machines are equipped with numerous sensors, granting them the ability to communicate and generate invaluable data. The logs capturing the performance of a single machine alone can yield approximately 5 gigabytes (GB) of data per week. To put it in perspective, this amounts to a colossal 5 million GB, equivalent to over 300,000 16 GB iPhones. This exponential growth in unstructured data has become both a boon and a bane, especially when 80% of it is unstructured and a mere 12% analyzed. Malicious actors, armed with sophisticated tools and stealthy techniques, can easily exploit sensitive data hidden in this vast sea of data, orchestrating cyberattacks that can paralyze entire manufacturing ecosystems. The risks of unstructured data within Industry 4.0 has thus transformed the manufacturing landscape into a treacherous domain, demanding robust cybersecurity measures and a vigilant mindset to safeguard the digital future.
Solution
- Know the data about your data: Metadata serves as a vital tool for acquiring a comprehensive understanding of data by offering descriptive information. It enables insights into various characteristics, including file ownership, creation and access timestamps, file types, and sizes. Manufacturers can then categorize, tag, and index data based on its relevance, categorizing it into hot, cold, and ROT (Redundant, Outdated, and Trivial) and take necessary actions such as archival, deletion, and data quarantining, thereby effectively managing the ever-expanding volumes of unstructured data.
- Identify Sensitive Data: Content analytics play a vital role in identifying patterns, anomalies, and potential threats within unstructured data. By leveraging advanced AI and machine learning algorithms, content analytics can scan vast volumes of data in real-time to filter sensitive or private information from unstructured data file content and ensure maximum accuracy. Additionally, it uses advanced, multi-level logical expressions and a combination of logical operators to generate actionable data-driven insights into risk exposure with descriptive and diagnostic analytics, providing an easy means of quantifying that risk. They can then reduce exposure and risk of rogue data usage by implementing data quarantining, intelligent file re-permissioning, access control, and immutable audit reporting.
- Get a holistic view of your datasphere: Context analytics takes data analysis a step further by considering the contextual information surrounding manufacturing processes. By analyzing data from multiple sources, including operational technology systems, IoT devices, and cybersecurity logs, context analytics can uncover hidden relationships and correlations. This holistic view provides manufacturers with invaluable insights into the entire manufacturing ecosystem, enabling them to identify vulnerabilities, anticipate potential risks, and formulate effective security strategies.
2. Connectivity: A Double-Edged Sword:
Industry 4.0 thrives on the seamless interconnectivity of devices, machinery, and systems. While this enables real-time data exchange and enhances operational efficiency, it simultaneously expands the attack surface for cybercriminals. With more access points, including IoT devices, sensors, and interconnected networks, the potential entry points for cyber attacks multiply. Without robust security measures, these interconnected devices become vulnerable, allowing cybercriminals to exploit weak links and infiltrate manufacturing systems.
Solution:
- Implement Robust Network Segmentation: By dividing the network into smaller segments, manufacturers can limit the spread of cyber attacks and mitigate potential damages. Compartmentalizing the systems reduces the attack surface and prevents unauthorized access across the entire network.
- Strengthen Access Control Measures: Implementing robust access control measures helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. This includes implementing strong authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and regular review of user access privileges. By limiting access to data based on the principle of least privilege, manufacturers can reduce the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access.
3. Legacy Systems and Inadequate Security:
Many manufacturing facilities still rely on legacy systems, which were not designed with cybersecurity in mind. These outdated technologies often lack the necessary security features, making them easy targets for cybercriminals. Furthermore, integrating legacy systems with modern technologies during the transition to Industry 4.0 creates additional vulnerabilities. Inadequate security measures, outdated software, and lack of regular updates make these systems attractive targets for hackers seeking to gain unauthorized access or disrupt operations.
Solution:
- Modernize and Upgrade Legacy Systems: Gradually replacing outdated systems with modern, secure technologies ensures a stronger defense against cyber threats. This includes migrating to newer operating systems, incorporating advanced encryption methods, and implementing security protocols designed for Industry 4.0 environments.
- Conduct Regular Security Assessments: Regularly assessing the security posture of legacy systems helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning can reveal potential entry points for cybercriminals, enabling organizations to address these issues proactively.
- Conduct Regular Data Backup: Implementing regular data backup processes is vital for ensuring data availability and resilience. Backup solutions should follow the 3-2-1 rule, which involves creating at least three copies of critical data stored on two different media types, with one copy stored offsite or in the cloud. Regularly testing the data restoration process is equally important to validate the integrity and effectiveness of backups.
4. Increased Data Exposure:
Industry 4.0 generates vast amounts of data through interconnected devices, smart sensors, and cloud computing. While this data is invaluable for optimizing production processes and making informed decisions, it becomes a prime target for cybercriminals. The theft, manipulation, or destruction of critical data can have severe consequences, ranging from financial losses to compromising product quality, supply chain disruptions, and even endangering human safety. The more data that Industry 4.0 generates, the greater the challenge of securing it from malicious actors.
Solution:
- Implement End-to-End Encryption: Encryption is a critical component of data storage strategies. It ensures that data is rendered unreadable to unauthorized parties. Manufacturers should implement encryption both at rest (data stored on storage devices) and in transit (data being transmitted between systems) to protect sensitive information. Strong encryption algorithms and key management practices should be employed to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of data.
- Deploy Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions: DLP solutions monitor and control data movements within the manufacturing environment, preventing unauthorized data transfers and detecting suspicious activities. They provide an additional layer of protection, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
5. Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness and Skills:
As the manufacturing sector embraces digital transformation, the demand for cybersecurity professionals has skyrocketed. Unfortunately, there is a significant shortage of skilled personnel with expertise in both cybersecurity and manufacturing. This skills gap leaves many manufacturing organizations ill-prepared to tackle the ever-evolving cyber threats. Without proper cybersecurity training, awareness, and protocols, employees may inadvertently become unwitting accomplices to cybercrimes, falling prey to social engineering tactics or failing to recognize and report potential vulnerabilities.
Solution:
- Conduct Regular Cybersecurity Training: Organizations should invest in comprehensive cybersecurity training programs for all employees, including awareness sessions on identifying phishing attacks, social engineering techniques, and best practices for data protection. Promoting a culture of cybersecurity awareness helps employees become the first line of defense against cyber threats.
- Collaborate with Educational Institutions: Partnering with universities, technical schools, and training centers can help bridge the skills gap in cybersecurity for the manufacturing sector. Supporting programs that offer specialized training and certifications can contribute to the development of a skilled workforce equipped to address Industry 4.0 security challenges.
- Be Proactive in Disaster Recovery Planning: Manufacturers should develop comprehensive disaster recovery plans that outline steps to recover data and restore critical systems in the event of a cyber-attack or other disruptive incidents. This includes defining recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) to guide the recovery process. Regular drills and simulations should be conducted to ensure the readiness and effectiveness of the disaster recovery plan.
6. Targeting Operational Technology (OT):
Industry 4.0 blurs the boundaries between information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) systems. Traditionally, OT systems were isolated from external networks, reducing the risk of cyber attacks. However, the convergence of IT and OT in Industry 4.0 exposes manufacturing processes and critical infrastructure to cyber threats. Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in OT systems to disrupt production lines, manipulate industrial processes, or cause physical damage to machinery, leading to substantial financial losses and safety hazards.
Solution:
- Implement Segregated Networks for OT Systems: Keeping OT systems separate from IT networks helps isolate critical industrial processes from potential cyber-attacks. By employing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure gateways, organizations can establish barriers between IT and OT environments, limiting unauthorized access.
The Data Dynamics Advantage
Data Dynamics Inc. can play a significant role in assisting manufacturing companies in maintaining effective data management strategies to enhance cybersecurity. Here are some ways Data Dynamics Inc. can help:
- Unified Data Management: Data Dynamics is a leading provider of enterprise data management solutions, helping organizations structure their unstructured data with their Unified Unstructured Data Management Platform. The platform encompasses four modules- Data Analytics, Mobility, Security, and Compliance. Proven in over 26 Fortune 100 organizations, the Platform uses a blend of automation, AI, ML, and blockchain technologies and scales to meet the requirements of global enterprise workloads. With Data Dynamics, enterprise customers can eliminate the use of individual point solutions with siloed data views. Instead, they can utilize a single software platform to structure their unstructured data, unlock data-driven insights, secure data, ensure compliance and governance and drive cloud data management.
- Data Storage Management: Data Dynamics Inc. offers comprehensive data storage management solutions specifically designed for manufacturing companies. These solutions provide visibility and control over data storage infrastructure, allowing organizations to monitor and manage their data storage environment effectively. This includes features such as data classification, data movement, and policy-based automation, enabling organizations to optimize storage resources and enhance security. Learn more about StorageX.
- Data Security and Compliance: Our unified data management platform incorporates robust security features to ensure data protection and compliance with industry regulations. These features may include data encryption, access controls, and data integrity checks. By implementing these security measures, manufacturing companies can safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access, maintain data privacy, and meet compliance requirements. Read more about our Security Suite here.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Effective data lifecycle management is essential for maintaining data storage strategies that align with cybersecurity objectives. Our platform enables manufacturing companies to define data lifecycle policies, automate data movement and archiving, and efficiently manage data retention and disposal. This helps organizations reduce the risk of data breaches, optimize storage costs, and ensure compliance with data governance regulations. Check out Data Dynamics’ Data Management Platform for more information.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Data Dynamics Inc. offers solutions for disaster recovery and business continuity planning. These products help manufacturing companies create comprehensive disaster recovery strategies, including backup and recovery capabilities. By implementing robust backup solutions, organizations can protect critical data and systems, minimize downtime, and ensure swift recovery in the event of a cyber-attack or other disruptive incidents.
- Analytics and Insights: The platform incorporates analytics and reporting capabilities, providing valuable insights into data storage environments. These insights enable manufacturing companies to identify vulnerabilities, assess storage performance, and detect anomalies that may indicate potential security threats. By leveraging these analytics, organizations can proactively address security gaps and enhance their cybersecurity defenses. Read about our Analytics Suite here.
To learn more about how Data Dynamics can help your enterprise secure your data ecosystem, please visit – www.datadynamicsinc.com or contact us at solutions@datdyn.com I (713)-491-4298.






