According to the Ponemon Institute and Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, the health industry experiences more data breaches than any other sector. This is largely due to the sensitive nature of healthcare data, which includes personal information like medical histories and insurance details that hackers and cybercriminals find valuable for fraudulent activities such as identity theft and insurance scams. Additionally, many healthcare organizations have outdated security measures and legacy computer systems that can be easily exploited by cybercriminals. A Q1 2022 report by IT Governance found that healthcare and health sciences accounted for 26% of all data breaches, with 65 incidents reported. By the end of the year, the number of breaches had skyrocketed to 658, with 78.5% of them due to hacking or IT incidents. Back in 2018, healthcare data breaches of 500 or more records were being reported at a rate of about one per day. But since then, things have taken a turn for the worse. In fact, the rate of such breaches has more than doubled in just five years. Today, in 2022, we’re seeing an average of 1.94 healthcare data breaches of 500 or more records reported each day.
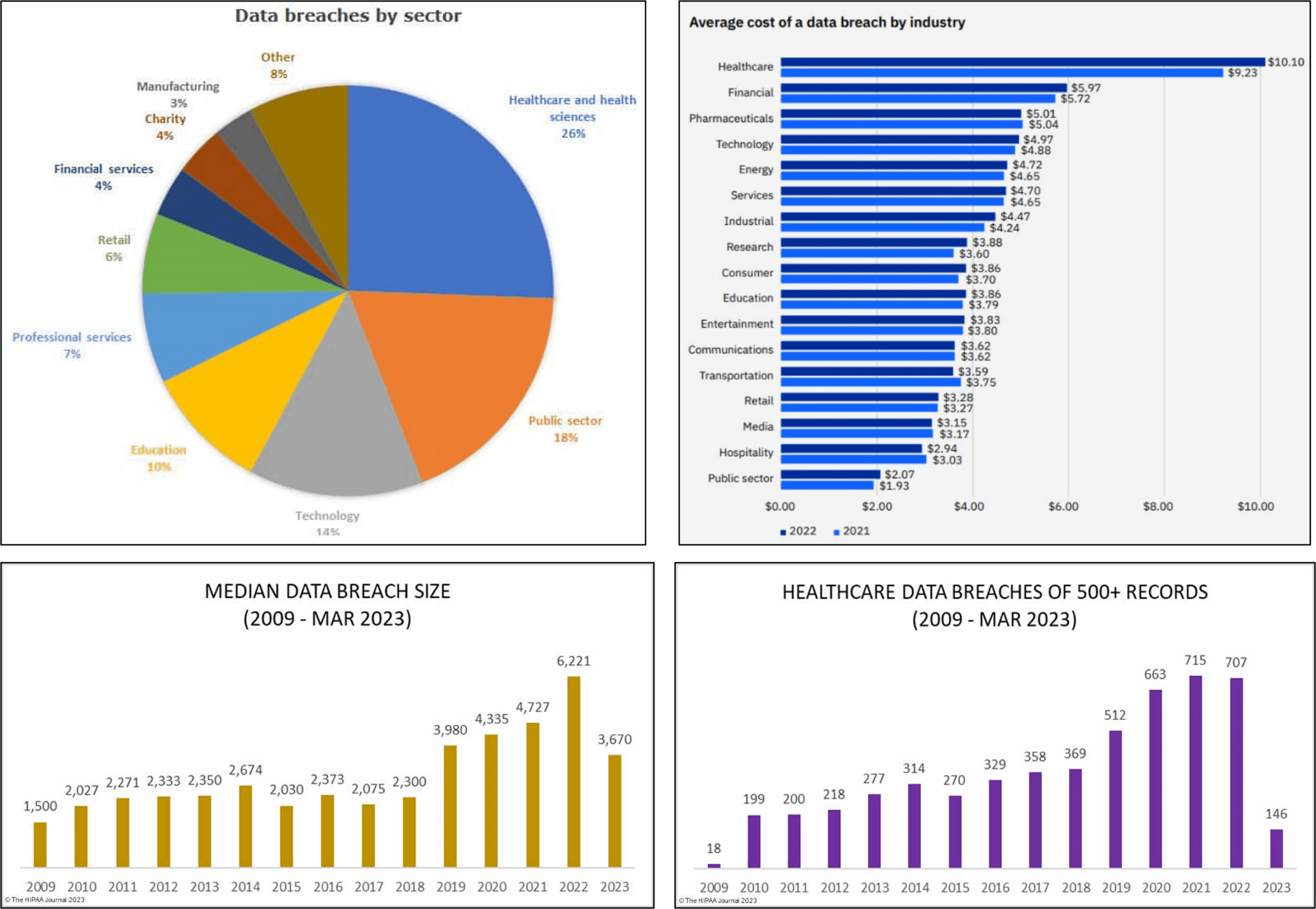
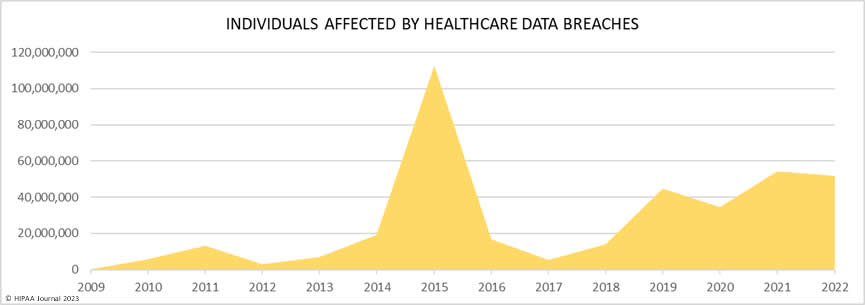
The consequences of healthcare data breaches can be serious, resulting in reputational damage, financial loss, and legal trouble. In fact, the average cost of a data breach is $4.24 million, with healthcare data breaches costing an average of $408 per record, which is three times higher than the cross-industry average. Healthcare data breaches also have a significant impact on consumers, with over 5,150 breaches reported between 2009 and 2022 resulting in the exposure of more than 382 million healthcare records, equivalent to more than 1.2 times the US population.
Here are some examples of significant data breaches in healthcare in the last 5 years:
- Anthem
Anthem is one of the largest health insurers in the United States, serving millions of customers. In 2015, Anthem suffered a massive data breach that exposed sensitive information belonging to nearly 80 million people. The hackers responsible for the breach gained access to names, birth dates, social security numbers, and other personal information. Anthem responded quickly by investigating the breach and notifying affected individuals. The company also offered free credit monitoring services to all impacted customers.
Despite these efforts, the fallout from the Anthem data breach was significant. Customers were understandably upset and concerned about their privacy and security. Moreover, there were concerns about how such a large-scale hack could happen in the first place.
The incident served as a reminder that no company – even those with significant resources – is immune to cyber-attacks. It highlighted how important it is for healthcare organizations to invest in robust cybersecurity measures and protocols to protect patient data from falling into malicious hands. In response to this incident, among others like it within healthcare systems across America since then, they have invested more time and resources into securing their networks from future breaches so that sensitive medical records are safeguarded against theft or hacking attempts.
- Premera
Premera Blue Cross is a healthcare company that provides insurance to millions of individuals across the United States. In 2015, it suffered one of the largest data breaches in history, affecting over 11 million people. The breach exposed sensitive information such as names, social security numbers, and bank account details. The attack was carried out by hackers who accessed Premera’s systems through a phishing email. This highlights the need for companies to educate their employees on cybersecurity best practices and to implement multi-factor authentication measures.
Following the breach, Premera faced numerous lawsuits from affected individuals and paid hefty fines imposed by regulators. The incident also damaged its reputation and eroded trust among its customers. Premera has since enhanced its cybersecurity posture, investing in new technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) for threat detection and prevention. It has also increased employee training on cyber threats.
However, it serves as a reminder that no organization is immune to cyberattacks, particularly those handling sensitive personal data like healthcare providers. Companies must remain vigilant against emerging threats and proactively protect themselves and their customers’ data.
- Excellus
Excellus is a health insurance company based in New York that suffered a data breach in 2015. The breach affected around 10 million of its members, including customers and employees. The attackers accessed the company’s IT systems and gained unauthorized access to sensitive personal information such as names, addresses, birth dates, social security numbers, financial information, and medical records. The attack on Excellus was considered one of the largest healthcare data breaches. It took the company over two years to discover the breach after it occurred, which raised concerns about its security protocols. Investigation revealed that hackers used malware to infiltrate Excellus’ network undetected for months.
The consequences of this breach were severe for both Excellus and its customers. Customers’ private data was exposed, putting them at risk for identity theft or other fraudulent activities, while Excellus faced multiple lawsuits alleging negligence in protecting their customers’ confidential information. In response to this incident, Excellus implemented several new measures to improve its cybersecurity posture, such as installing more sophisticated antivirus software and implementing employee training programs on cyber threat awareness.
- UPMC
In 2021, one of the biggest healthcare data breaches was suffered by UPMC. The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center is a leading provider of healthcare services in Pennsylvania and beyond. Unfortunately, it was targeted by hackers who gained access to sensitive patient information. The breach affected more than 36,000 patients with compromised personal and medical information. This included names, birth dates, Social Security numbers, diagnosis codes, and other sensitive data that could be used for identity theft or fraud.
UPMC took immediate action to contain the damage and notify affected patients. However, the incident highlights the ongoing threat of cyber attacks on healthcare providers. As technology advances at an ever-increasing pace, so too must security measures keep up with new threats.
- Community Health Systems
Community Health Systems (CHS) data breach took place between April and June 2014. The attackers could steal personal information like names, addresses, birth dates, and social security numbers of 4.5 million patients. The CHS attack demonstrated how devastating a data breach can be for patients and providers. It resulted in massive financial losses and eroded patient trust in the healthcare system.
These five data breaches are a stark reminder that cybersecurity must remain at the forefront of every healthcare organization’s agenda. They must implement robust security measures to secure their networks against cyber threats. Otherwise, they risk losing sensitive patient information while facing reputational damage that could take years to recover from finally!
Top 5 data storage and backup device security risks that must be addressed
Today, approximately 30% of the world’s data volume is being generated by the healthcare industry. That’s a lot of data, and it needs to be stored somewhere reliable and secure. That’s where enterprise storage devices come in. These devices, often in the form of network-attached storage (NAS) or storage area networks (SAN), can handle a massive amount of data and keep things running smoothly. They provide high-performance storage capabilities, advanced data protection features, and scalable storage capacity to meet the needs of businesses with large amounts of data. Enterprise storage devices can store various types of data, including files, documents, images, videos, and databases. Additionally, backup devices are a crucial addition to the tech toolkit as they’re designed to create duplicates of important data and store them in a separate location in case anything goes wrong. With the help of enterprise storage and backup devices, businesses can keep their data safe and sound.
But here’s the thing: while enterprise storage and backup devices are crucial for keeping business operations running smoothly, they can also make companies more susceptible to data breaches. These devices can be targets for cybercriminals who want to steal or manipulate sensitive data. If these devices aren’t properly secured, they can be vulnerable to all sorts of cyberattacks, such as malware infections, data theft, and ransomware attacks.
According to Continuity’s State of Storage and Backup Security Report 2023, the average enterprise storage and backup device has 14 vulnerabilities. And three of those are high or critical risk, which could pose a significant threat if exploited. This indicates that there’s a considerable gap in the state of enterprise storage and backup security compared to other layers of IT and network security. The report detected a total of 9,996 security issues, including vulnerabilities and security misconfigurations, that were not adequately addressed, spanning over 270 security principles. The concerning part is that this year’s report is almost identical to last year’s, indicating little has been done to address this high-risk area. Unpatched vulnerabilities in storage and backup systems are the primary targets for most ransomware, and traditional vulnerability management tools do not cover these systems well. Continuity warns that businesses need to take steps to address these vulnerabilities and ensure that their enterprise storage and backup devices are adequately secured to prevent data breaches.
Here are the top five storage and backup device security risks detected by Continuity in its latest analysis:
- Insecure network settings (use of vulnerable protocols, encryption ciphers): Insecure network settings, such as vulnerable protocols or weak encryption ciphers, can also cause data breaches in healthcare. Hackers and cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in these protocols and ciphers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive patient information. For example, using outdated protocols, such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and early versions of Transport Layer Security (TLS), can make a network vulnerable to attacks. Similarly, weak encryption ciphers, such as those that use short keys or outdated algorithms, can make it easier for hackers to decrypt the data.
- Unaddressed Common Vulnerability and Exposures (CVEs): CVEs are known security vulnerabilities in software and hardware systems that can be exploited by hackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive patient information. Healthcare organizations can leave their systems open to attack if they fail to address these vulnerabilities. For example, if a healthcare organization fails to apply a security patch for a known vulnerability in its EHR system, a hacker could exploit it to access patient data.
- Access rights issues (over-exposure): Over-exposure occurs when individuals are granted access to sensitive patient information that they do not need to perform their job duties. This can occur when healthcare organizations fail to properly manage access rights or when employees abuse their access privileges. For example, a receptionist with access to patient records may inadvertently disclose sensitive information to unauthorized individuals, or an employee with malicious intent could steal patient data.
- Insecure user management and authentication: Weak user authentication, such as using easily guessable passwords or failing to implement multi-factor authentication, can make it easier for hackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive patient information. Additionally, poor user management practices, such as failing to disable accounts of former employees, can leave healthcare organizations vulnerable to insider threats. For example, a former employee with access to patient data could intentionally cause a data breach or inadvertently cause a breach through negligence.
- Insufficient logging and auditing: Without proper logging and auditing, it can be difficult for healthcare organizations to detect and respond to security incidents, such as unauthorized access attempts or data breaches. Insufficient logging can occur when healthcare organizations fail to record important security events, such as failed login attempts, changes to user permissions, or suspicious network activity. Without this information, it can be challenging to identify potential security risks or investigate security incidents. Inadequate auditing can occur when healthcare organizations do not regularly review and analyze their security logs to identify security incidents or potential security risks.
How can healthcare organizations address these risks?
Healthcare organizations can take several steps to address data storage risks and minimize the risk of data breaches. Some key strategies include:
- Update network settings: By now we all are aware that healthcare organizations are constantly grappling with the challenge of safeguarding sensitive patient information from cyber threats. One of the critical steps in ensuring the security of healthcare data is to regularly update network settings. By doing so, organizations can take advantage of the latest security patches and features to protect their systems against vulnerabilities that may be exploited by cybercriminals. Additionally, using strong encryption protocols and ciphers can further enhance the security of patient data by making it more difficult for unauthorized parties to access it. Secure configurations, such as disabling unnecessary network services and ports, can also help to reduce the attack surface and minimize the risk of a data breach. By taking a proactive approach to network security, healthcare organizations can ensure that they are well-prepared to defend against the constantly evolving threat landscape and protect their patients’ sensitive information.
- Monitor CVEs: In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, it is critical for healthcare organizations to maintain vigilance and promptly respond to vulnerabilities. Continuous monitoring of CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) is necessary to detect and address any identified weaknesses in the system. Rapid action through security patches, software updates, or other remediation measures is crucial to prevent exploitation by cybercriminals. Healthcare organizations should also have robust vulnerability management programs that encompass regular scanning, penetration testing, and risk assessment to proactively manage vulnerabilities and minimize risks to patient data.
- Implementing strong access control policies: To enhance the security of sensitive patient information, healthcare organizations must implement robust access control policies. This can involve measures such as multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and strong password requirements. Regular audits of user access rights can also help ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information. Additionally, providing regular training to employees on data security best practices can help prevent access rights issues and minimize the risk of a data breach. Healthcare organizations can educate employees on the importance of protecting sensitive information and the potential consequences of a breach. This can include discussing topics such as phishing attacks, password hygiene, and the proper handling of confidential information.
- Implementation of strong authentication protocols: To further enhance security measures in healthcare organizations, the implementation of strong authentication protocols is essential. One of them is strong passwords that are essential for ensuring secure user authentication. Secondly, multi-factor authentication provides an additional layer of security, requiring users to provide two or more pieces of evidence to verify their identity. Also, it is important to drill in the message with regular security training and awareness campaigns can help educate employees about the importance of strong user authentication and user management practices. Finally, healthcare organizations should regularly audit user accounts to ensure that access is limited to only authorized personnel. This can involve disabling accounts of former employees, conducting periodic reviews of user access rights, and implementing a principle of least privilege, where employees only have access to the data needed to perform their job duties.
- Regular auditing: Regular auditing is a critical aspect of maintaining the security of healthcare organizations’ sensitive data. It helps detect security incidents early and provides valuable information for incident response and remediation. To ensure effective auditing practices, healthcare organizations should implement comprehensive logging and auditing policies and procedures. One way to accomplish this is by configuring systems to capture important security events, such as login attempts and changes to access controls. Additionally, healthcare organizations should regularly review security logs to detect any suspicious activity, analyze logs to identify potential security incidents or risks, and respond promptly to any identified threats.
Moreover, having a well-defined incident response plan is also essential. This plan should include processes for responding to security incidents identified through logging and auditing. It should define the roles and responsibilities of incident response team members, as well as specific actions to take in response to different types of security incidents. Regular training and testing of the incident response plan can help ensure that healthcare organizations are prepared to respond effectively to security incidents.
Three Effective Techniques for Enhancing Security
The average patient generates an impressive 80 megabytes of clinical data annually. This includes a wide range of information such as sensor readings, clinical notes, lab tests, medical images, medication lists, and insurance details. Now, multiply this by the total number of patients around the world, and the amount of data generated is mind-boggling!
However, here’s the catch – not all of this data is organized systematically or standardized. This is what we call unstructured healthcare data, and it’s causing significant problems in data security. In fact, analysts at Gartner estimate that upward of 80% of enterprise data today is unstructured. Protecting and managing this type of data can be quite a challenge due to its lack of organization, inconsistent formatting, and sheer volume.
But that’s not all – unstructured healthcare data often contains sensitive personal and medical information that can be targeted by hackers for identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious purposes. And with a variety of data sources and no standardization, creating effective security protocols is not an easy feat. This leaves healthcare organizations vulnerable to data breaches, putting patient data at risk.
In order to safeguard patient information from unauthorized access and improper usage, healthcare providers must first find a way to structure unstructured data, and the following three approaches can be highly effective:
- Metadata Analytics: Metadata refers to the data that describes other data, such as the author, date of creation, location, file type, etc. Analyzing metadata can help organizations detect anomalies or patterns that could indicate a security breach. For instance, if a user is accessing files from an unusual location or at an odd time of day, it could indicate that their account has been compromised. Metadata analytics can also be used to monitor network traffic and detect suspicious behavior, such as excessive data transfers or communication with known malicious IP addresses.
- Content Analytics: Content analytics involves analyzing the actual content of files or communications to detect security threats. This can include text, images, audio, and video data. For example, content analytics can be used to detect the presence of malware in files by scanning for known signatures or behavior patterns. It can also be used to detect sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers, that may be included in files or emails.
- Context Analytics: Context analytics involves analyzing data in the context of other data to detect security threats. For example, it may involve analyzing a user’s behavior patterns to detect if they are accessing files they don’t usually access or attempting to download large amounts of data. It can also involve analyzing network traffic to detect unusual patterns, such as a sudden surge in traffic from a particular location.
The Data Dynamics Advantage
The Data Dynamics unified data management platform is a comprehensive and efficient solution that empowers enterprises to optimize the value of their unstructured and voluminous data while maintaining top-notch security measures to ward off potential data breaches. By leveraging metadata, content and context analytics to categorize, tag, and index data, the platform can identify any personally identifiable information (PII/PHI) and apply appropriate security controls such as data remediation, data quarantining, access control management, and immutable audit logging. Additionally, the platform streamlines data management by providing automated access control and file security management within a single software. This eliminates the need for siloed software and multiple vendors, making it an all-in-one solution that addresses every aspect of data management. The platform’s advanced features allow organizations to manage and transform their enterprise data while preserving its integrity, making it an ideal solution for organizations seeking to enhance their data management practices, protect sensitive data, and prevent data breaches.
To learn more about Data Dynamics’ Analytics & Security suite, please visit – www.datadynamicsinc.comor contact us at solutions@datdyn.com I (713)-491-4298.






