- The digital era is redefining privacy, with 84% of adults feeling they have little control over their personal data. This poses challenges for governments and corporations, prompting initiatives like data localization and centralized identity management to address growing concerns.
- Consumers are increasingly aware of data ownership. They demand transparency, control, and security over personal data.
- Companies falling behind in privacy initiatives face trust loss, with 74% of consumers taking steps to protect their online privacy.
- The crucial step is adopting cutting-edge data management approaches that enable organizations to glean maximum insights from their data while prioritizing the protection of citizens’ privacy and data rights.
In an era where the digital world reigns supreme, the concept of privacy has taken on a whole new dimension. Governments and corporations around the world are wrestling with the challenges and responsibilities associated with citizens’ right to digital privacy. In this blog, we’ll explore the changing landscape of digital privacy, government initiatives such as data localization and centralized identity management, and the increasing demands of consumers for greater transparency and control over their personal data.
The Digital Privacy Revolution and Citizens’ Right to Digital Privacy
In recent years, digital privacy has become a hot-button issue, driven by the fact that an ever-increasing portion of our lives is now lived online. With the pervasive integration of the internet and digital technologies into virtually every aspect of our existence, we’ve seen an unprecedented surge in the amount of personal information being generated and shared online. This transition to a digital-centric lifestyle has ignited heightened concerns regarding the collection, storage, and utilization of our personal data.
As our lives have become increasingly intertwined with the digital world, a fundamental realization has taken hold: the digital landscape has the potential to both empower and infringe upon our privacy rights. This dichotomy has prompted individuals and societies to reevaluate the boundaries of digital privacy, particularly in the context of how our personal information is managed and protected. There is a heightened awareness in consumer behavior as people begin to scrutinize how their personal data is collected, processed, and shared. The crux of this transformation revolves around the concept of data ownership.
Governments worldwide have been swift to respond to these mounting concerns. Recognizing the importance of safeguarding citizens’ digital privacy, they have implemented various strategies to exert greater control over the vast troves of data generated within their national borders. Two key strategies at the forefront of this effort are data localization and centralized identity management systems to fortify data ownership and control.
Data Ownership: Transforming Consumer Behavior
Data ownership is the bedrock upon which digital privacy stands. In essence, it asserts that individuals should have the ultimate control and authority over the personal information they generate or provide online. This information encompasses a wide array of data, including personal details, preferences, online behaviors, and more. It’s the data trail we leave behind as we interact with digital platforms, devices, and services.
The digital ecosystem, powered by data-driven technologies and the proliferation of the internet, constantly collects, processes, and utilizes this personal data. However, the crucial question arises: who owns this data? Is it the individual who generates it, or do the companies and organizations collecting it claim ownership? The answer to this question forms the foundation of the debate surrounding digital privacy.
The growing awareness of data ownership has transformed consumer behavior in profound ways.
Consumers now seek greater transparency and control over their personal data. They want to know where their data is being stored, how it is being used, and who has access to it. This shift in attitude is a direct response to the realization that personal data, if mishandled or exploited, can have far-reaching consequences for individuals, including identity theft, financial fraud, and the erosion of personal privacy. This demand for digital privacy translates into five key aspects of data rights:
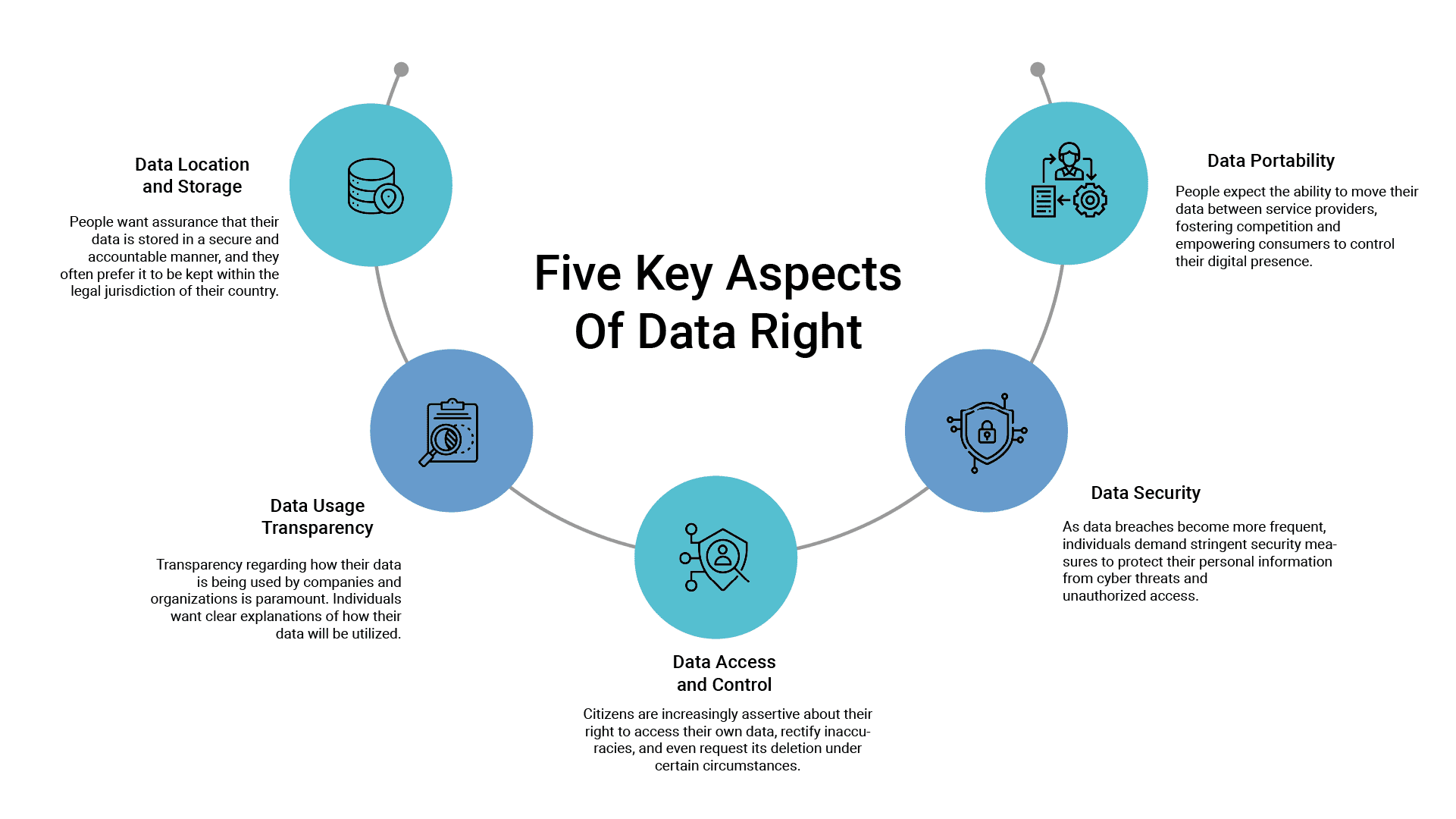
Government entities worldwide have recognized the importance of safeguarding citizens’ digital privacy in the face of growing concerns about data breaches, online surveillance, and the misuse of personal information. To address these issues, various initiatives and regulations have been put in place to protect citizens’ digital privacy. Here are some of the key initiatives being taken by governments:
- Data Protection Laws: Many countries have implemented comprehensive data protection laws that govern how personal data should be collected, processed, and stored. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union is one of the most prominent examples, setting stringent standards for data protection and privacy. Data protection laws can help rebuild trust, potentially increasing data-sharing comfort.
- Data Localization Requirements: Some countries have imposed data localization requirements, mandating that certain types of data must be stored within the country’s borders. This is often done to ensure that the government has jurisdiction over the data and can enforce local privacy laws.
- Privacy Impact Assessments: Government organizations encourage or require organizations to conduct privacy impact assessments (PIAs) before implementing new technologies or data processing practices. PIAs help identify and mitigate privacy risks associated with these initiatives.
- Centralized Identity Management: Centralized identity management systems, often managed by governments, are being implemented to provide citizens with secure and standardized digital identities. These systems aim to protect against identity theft and fraud.
- Transparency and Consent Requirements: Government entities are pushing for greater transparency in data processing practices. They require organizations to inform users about how their data is being used and obtain explicit consent for data collection and processing.
- International Data Transfer Agreements: To facilitate the flow of data across borders while maintaining privacy standards, government organizations are engaging in international data transfer agreements and mechanisms, such as Privacy Shield (between the EU and the U.S.) and standard contractual clauses.
- Cybersecurity Regulations: Strict mandates are being enforced about implementing cybersecurity regulations to ensure that organizations take adequate measures to protect the data they collect and process from cyber threats and breaches.
Companies that lag behind in initiatives aimed at safeguarding digital privacy may encounter a range of consequences with both reputational and financial implications. In an era where the importance of digital privacy is continuously growing, failing to keep pace with evolving privacy standards and expectations can result in the loss of customer trust, potential regulatory penalties, data breaches, negative publicity, and a competitive disadvantage as privacy-conscious consumers opt for companies that prioritize data protection. Moreover, companies may face increased operational costs, limited market expansion opportunities, consumer backlash, and legal liabilities, all of which can severely impact their bottom line and long-term sustainability. Employee morale and the ability to attract top talent may also suffer as individuals seek to align with organizations that demonstrate a commitment to digital privacy and data security.
Seven Best Practices for Safeguarding Citizens’ Privacy and Data Rights
Ensuring robust data privacy standards is imperative in today’s data-driven landscape, and it extends far beyond merely storing data securely. Here, we delve into key best practices that go hand in hand with safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining user trust.
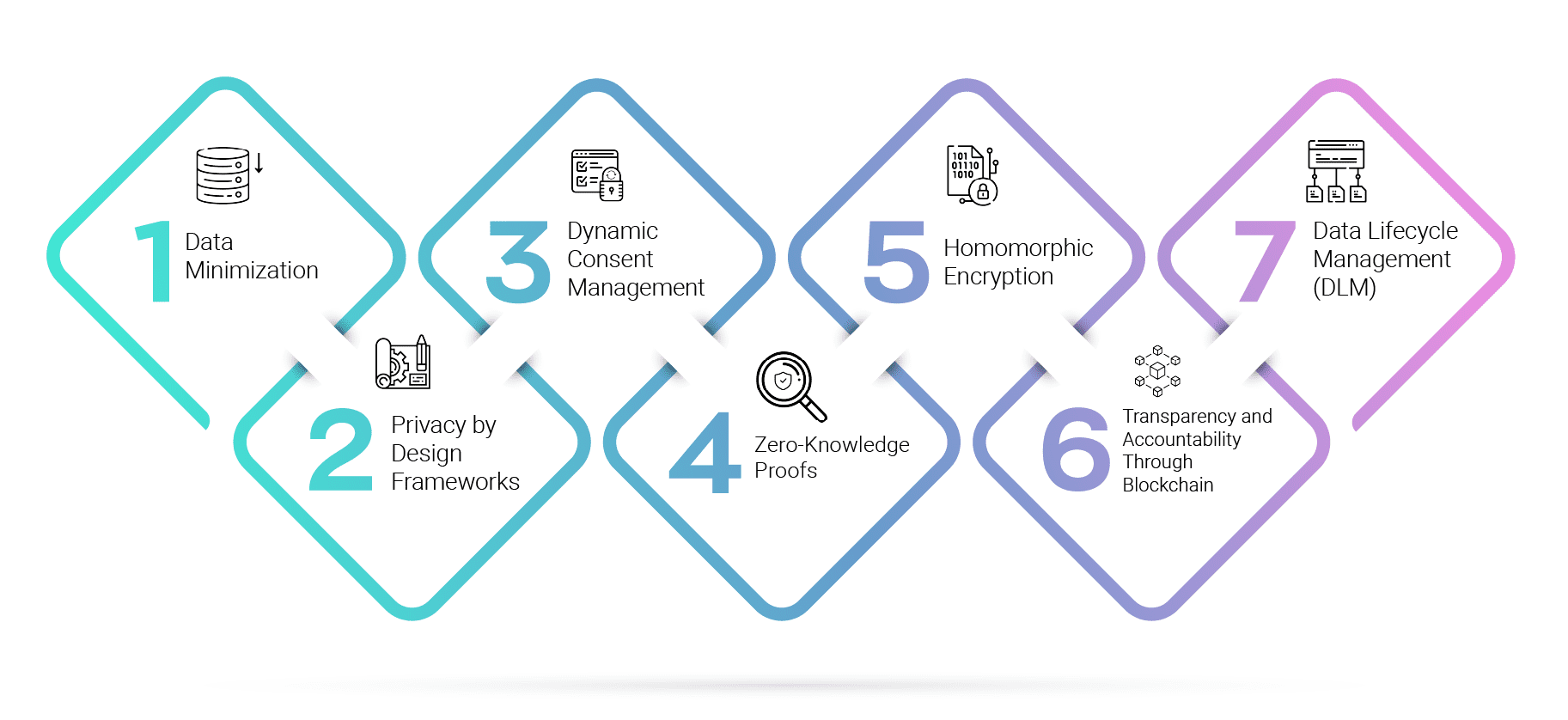
1. Data Minimization
A survey by the International Association of Privacy Professionals found that GDPR compliance has resulted in a 40% reduction in the volume of personal data held by organizations.
Data minimization is a fundamental privacy principle that underpins responsible data handling. In this innovative approach, enterprises aim to collect and retain only the minimum amount of data necessary to achieve specific, predefined purposes. Rather than amassing vast datasets that may contain unnecessary personal information, organizations focus on targeted and purpose-driven data collection. For example, a tax authority may limit data collection to a citizen’s income and tax-related information, omitting the need for extensive financial history. Moreover, automatic data expiration and deletion protocols play a crucial role in ensuring that data is not stored indefinitely. By establishing clear retention policies, enterprises can maintain data only for the duration of its relevance, reducing the risk of misuse or breaches. Such strategies not only safeguard citizens’ privacy but also streamline data management and reduce storage costs, all while minimizing exposure to potential data breaches. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates data minimization. Companies operating in the EU must limit data collection to what is strictly necessary for the intended purpose.
2. Privacy by Design Frameworks
According to a study by the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP), organizations with a privacy-by-design approach experience 40% fewer data breaches compared to those that don’t prioritize privacy during development.
Privacy by Design stands as a visionary approach to data privacy, urging enterprises to weave privacy into the very fabric of their operations and services. This innovative framework encourages proactively embedding privacy considerations into the design and development of systems and processes, ensuring that data protection is not merely an afterthought but a fundamental component. In practical terms, this means that from the initial stages of conceiving a service or system, privacy is considered at every turn. For example, when designing a citizen-facing web portal, privacy features, such as robust encryption, user consent mechanisms, and data minimization strategies, are built into the platform’s core architecture. This approach ensures that data protection isn’t a separate layer but an integral part of the service, fostering trust among citizens that their personal information is handled with the utmost care. Privacy by Design thus represents a pioneering philosophy that reshapes the very nature of government operations, placing privacy at the forefront of service delivery. The Estonian government is a pioneer in privacy by design. Their e-residency program, which allows non-Estonians to access Estonian services and businesses online, incorporates strong privacy measures. They use blockchain technology to secure data and ensure transparency in data access and usage.
3. Dynamic Consent Management
A study by TrustArc found that 90% of consumers want the ability to easily manage their data privacy preferences, highlighting the demand for dynamic consent solutions.
Dynamic consent management platforms represent a groundbreaking approach to data privacy that empowers individuals with real-time control over their personal data usage. In these innovative systems, citizens can provide or revoke consent for various data processing activities as circumstances change. This real-time consent management allows for unprecedented granularity and transparency in data handling. For instance, a citizen can grant consent for a healthcare provider to access their medical records for a specific treatment, and later, they can promptly revoke that consent once the treatment is completed. To ensure transparency and traceability, blockchain technology is often integrated into these platforms. This granular approach to consent management not only places individuals in charge of their data but also fosters greater transparency and accountability in government data practices. It aligns data usage more closely with citizens’ preferences and evolving needs, ultimately promoting trust in government services. MyData.org, a global nonprofit, promotes the concept of individuals having control over their personal data. They advocate for dynamic consent mechanisms that put individuals in charge of how their data is used.
4. Zero-Knowledge Proofs
According to a report by Deloitte, 70% of enterprises plan to use zero-knowledge proofs or similar privacy-enhancing technologies to protect sensitive data by 2023.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs represent an ingenious cryptographic technique that plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive data during transactions and interactions. This innovative approach allows two parties to verify the accuracy of information without the need to disclose the actual data itself. In practical terms, it means that government entities can ascertain the validity of citizen data without the necessity of storing or exposing personal details. This is achieved through complex mathematical protocols that enable one party to prove knowledge of a specific piece of information without revealing the information itself. For instance, in an age verification scenario, a citizen could prove they are of legal drinking age without revealing their precise birthdate. Zero-Knowledge Proofs thus offer a powerful means to enhance data privacy, reducing the risks associated with traditional data exchanges while still facilitating trust and accuracy in government transactions. Zcash is a cryptocurrency that employs zero-knowledge proofs for transactions. It allows users to shield their transaction data while still verifying the validity of the transaction.
5. Homomorphic Encryption
The global homomorphic encryption market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 27.8% from 2021 to 2028, indicating a rising demand for privacy-preserving data processing solutions.
Homomorphic Encryption stands as a cutting-edge encryption method that finds critical applications in securing citizen data while enabling data analysis and processing. This advanced technique allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without the need to decrypt it first, preserving privacy while extracting valuable insights. Homomorphic Encryption is particularly invaluable when dealing with sensitive health or financial information, where privacy is paramount. For instance, in healthcare, researchers can perform statistical analyses on encrypted patient data without ever accessing the patients’ identifiable information. This not only ensures data privacy but also advances critical research without compromising sensitive data. Homomorphic Encryption thus serves as a beacon of innovation in the protection of citizen data, allowing governments to harness the power of data analytics while respecting individual privacy. Microsoft’s Azure Confidential Computing uses homomorphic encryption to protect data while it’s being processed in the cloud, ensuring privacy for sensitive workloads.
6. Transparency and Accountability Through Blockchain
A Gartner survey reveals that 75% of organizations plan to use blockchain for operational purposes, including data transparency and traceability, by 2023.
Blockchain technology is harnessed as an innovative solution to ensure transparency and accountability in government data handling. By implementing smart contracts and distributed ledger technology, governments can create immutable records of data access and usage. This transparency empowers citizens to audit who has accessed their data and for what purpose, instilling trust in government practices. For instance, in a public procurement process, blockchain can record each step of the process, from vendor submissions to contract awarding, ensuring transparency and accountability. It also reduces the potential for fraud or corruption. Moreover, blockchain’s decentralized nature means that data cannot be tampered with or deleted retroactively, enhancing the integrity of government records. Blockchain, as an innovative tool for data transparency, offers a robust solution to strengthen citizens’ confidence in enterprise data management practices. The state of Illinois in the USA has explored blockchain for recording land titles, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud in property transactions.
7. Data Lifecycle Management (DLM)
According to a study by IBM, organizations that implement effective Data Lifecycle Management practices can reduce data storage costs by up to 20% while simultaneously improving data security and compliance.
Data Lifecycle Management is a comprehensive and forward-thinking approach that governs the entire journey of data within an organization or government entity. This holistic strategy entails the systematic handling of data from its moment of creation through various stages of storage, utilization, and sharing, all the way to its eventual disposal or archiving. What makes DLM truly innovative is its emphasis on integrating privacy considerations at every step of this data journey, ensuring that data privacy remains a paramount concern from the moment data comes into existence to its ultimate deletion or archiving. For example, when enterprises collect citizen data for a specific purpose, DLM ensures that this data is stored securely and only used for its intended purpose. Once the data is no longer needed, DLM protocols guide its responsible disposal, ensuring that it isn’t retained indefinitely, thereby minimizing the risk of misuse or breaches. DLM serves as a visionary strategy that promotes responsible data handling while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations, culminating in enhanced data privacy for citizens throughout the entire data lifecycle. The Norwegian Data Protection Authority (Datatilsynet) implemented a robust DLM framework, including strict policies on data retention and secure disposal. This ensures that personal data is not retained longer than necessary and is safely disposed of when no longer needed.
These best practices collectively contribute to a comprehensive data privacy strategy that safeguards sensitive information, protects against potential breaches, and fosters user trust. Companies that prioritize data privacy beyond mere storage are better equipped to navigate the evolving landscape of data protection regulations and demonstrate their commitment to respecting user privacy rights.
The Data Dynamics Advantage
The growing demand for the “right to data” marks a significant shift in the digital landscape, opening up boundless opportunities for organizations to leverage data for informed decision-making and remarkable achievements. However, dealing with the immense volume of data generated every second can make the concepts of control, consent, and transparency seem daunting.
This is where Data Dynamics’ Unified Data Management Platform shines—a beacon of simplicity amidst the complexity, assisting enterprises in navigating the intricate terrain of consent management. Trusted by more than 28 Fortune 100 organizations, the platform comprises four essential modules: Data Analytics, Mobility, Security, and Compliance—all integrated into a single software architecture. By centralizing data from various sources and systems it simplifies the processes of data capture, storage, and oversight through a unified interface. This consolidation enables organizations to consistently and precisely comply with evolving data privacy regulations, regardless of the data collection channels used.
Thanks to this platform, companies can effortlessly monitor and audit data usage and ownership across their operations, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated legal repercussions. Furthermore, its analytical capabilities offer valuable insights into enterprise-sensitive data, data trends, and behaviors, assisting companies to remediate and secure their data while refining their overall practices to better align with customer preferences.
In essence, the Data Dynamics’ Unified Data Management Platform stands as a potent tool for businesses seeking to navigate the intricate landscape of Citizen Data Rights while concurrently delivering an exceptional and privacy-conscious experience to their clientele. To know more about Data Dynamics, visit www.datadynamicsinc.com or connect with us at solutions@datdyn.com / (713)-491-4298.






