Highlights:
- In the process of transitioning their operations to the cloud, the BFSI industry must tread carefully to avoid significant missteps that could result in unfavorable financial outcomes.
- A 2022 study conducted by RightScale found that a concerning 32% of cloud adoption projects end up in failure, with an additional 43% of respondents indicating that their organizations lacked a well-defined strategy for cloud adoption.
- Further amplifying this concern, research from CloudHealth highlights that a failed cloud adoption project comes with an average price tag of $10 million.
- The landscape is riddled with potential pitfalls that must be skillfully navigated during cloud adoption in order to sidestep becoming one of these unfortunate statistics. But what are these pitfalls, and how can they be seamlessly integrated into operations? Read on to find out.
In this Blog
The financial landscape is currently in the midst of a significant transformation as institutions eagerly embrace the possibilities offered by cloud technology. However, the path towards cloud migration comes with its own set of challenges, and if these are not skillfully managed, the consequences can be widespread and lasting.
In this blog, we’re about to delve into the complexities linked with migrating to the cloud within financial institutions. Our journey will involve an exploration of the top five hurdles that BFSI players have come across while embracing the cloud. By understanding the profound repercussions of these challenges, our goal is to offer five essential takeaways for each of these situations. These insights are designed to empower BFSI entities, enabling them to anticipate these challenges and navigate the transformative process with finesse, ultimately ensuring a successful progression through this evolutionary phase.
The 5 Biggest Mistakes in Cloud Adoption: Impact and Solutions
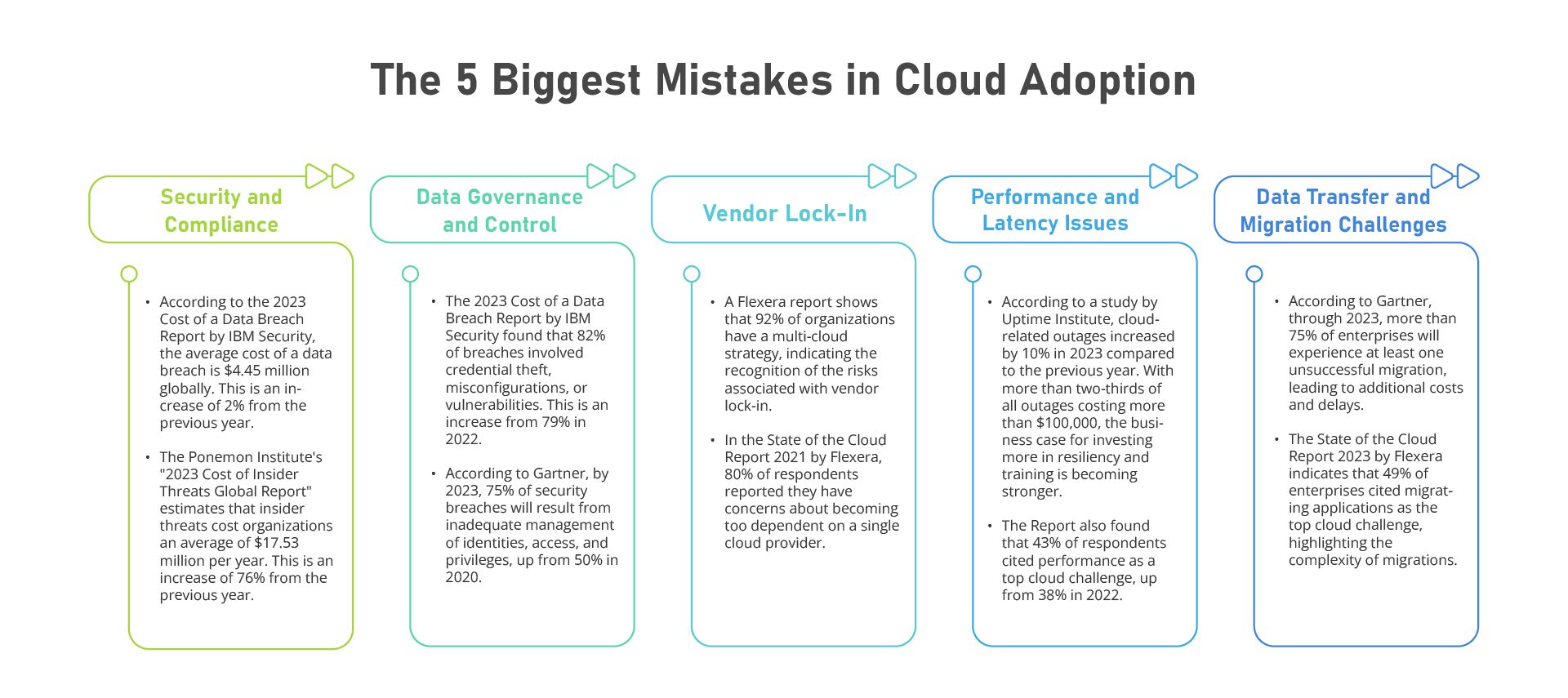
1. Security and Compliance
JPMorgan Chase & Co. is a prime example of the security risks banks face during cloud migration. In 2014, the bank moved a significant portion of its data to a public cloud without adequately securing it. As a result, hackers gained access to sensitive customer data, compromising personal information and financial details.
- According to the 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM Security, the average cost of a data breach is $4.45 million globally. This is an increase of 2% from the previous year.
- The Ponemon Institute’s “2023 Cost of Insider Threats Global Report” estimates that insider threats cost organizations an average of $17.53 million per year. This is an increase of 76% from the previous year.
Impact: The financial impact of the data breach is estimated to be $100 million. Additionally, JPMorgan also faced reputational damage and regulatory scrutiny. Regulatory authorities imposed fines, investigations were launched, and the incident created mistrust among customers, resulting in potential customer attrition.
Solution:
- Comprehensive Security Assessment and Strategy: Begin the cloud migration process with a thorough security assessment that identifies potential vulnerabilities, risks, and compliance requirements specific to the organization’s industry and data. Engage cybersecurity experts to conduct a detailed analysis of the existing infrastructure and data assets. Develop a comprehensive security strategy that outlines measures for data encryption, access controls, identity management, and threat detection. This strategy should be tailored to address both external and insider threats.
- Multi-Layered Data Encryption: Implement robust encryption mechanisms at multiple levels to safeguard sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Utilize industry-standard encryption protocols to ensure that data remains protected during transmission between on-premises systems and the cloud, as well as while stored within cloud environments. Employ strong encryption key management practices to prevent unauthorized access even in the event of a breach.
- Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection: Deploy advanced monitoring and threat detection tools that provide real-time visibility into cloud environments. Use technologies like intrusion detection systems, behavior analytics, and anomaly detection to identify and respond to suspicious activities promptly. By monitoring user behavior and system interactions, organizations can detect insider threats, unauthorized access, and potential breaches early, minimizing their impact.
- Access Controls and Identity Management: Implement strict access controls and robust identity management practices to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data and systems. Utilize techniques such as role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and least privilege principles to limit access rights based on job roles and responsibilities. Regularly review and update access permissions to align with organizational changes.
- Regular Compliance Audits and Training: Conduct regular compliance audits to ensure that cloud deployments adhere to industry regulations and internal policies. Collaborate with compliance experts to validate that security measures align with standards such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR. In addition, invest in continuous training and awareness programs for employees to educate them about security best practices, the importance of data protection, and the risks associated with insider threats.
2. Data Governance and Control
The Capital One breach in 2019 exposed the challenges of maintaining data governance in the cloud. A former employee exploited a misconfigured firewall to gain unauthorized access to sensitive customer data stored in the cloud. The incident highlighted the importance of proper data governance.
- The 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM Security found that 82% of breaches involved credential theft, misconfigurations, or vulnerabilities. This is an increase from 79% in 2022.
- According to Gartner, by 2023, 75% of security breaches will result from inadequate management of identities, access, and privileges, up from 50% in 2020.
Impact: The breach resulted in a significant financial hit for Capital One. They faced a settlement of $80 million to compensate the affected customers and address the regulatory repercussions. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, the total cost of the breach to Capital One was estimated to be $190 million.
Solution:
- Robust Cloud Architecture Design: Begin by designing a cloud architecture that prioritizes data governance and security. Collaborate with cloud architects and security experts to ensure that cloud environments are structured in a way that minimizes vulnerabilities and enforces strong access controls. Consider implementing a Zero Trust architecture that assumes no entity, whether inside or outside the network, can be trusted by default.
- Automated Configuration Management: Implement automated configuration management tools that ensure cloud resources are correctly configured from the outset and remain compliant with security standards. Continuous monitoring and auto-remediation mechanisms can promptly address misconfigurations or vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of unauthorized access resulting from human error.
- Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) and Least Privilege: Enforce strict RBAC and least privilege principles to control user access to data and resources within the cloud environment. Assign roles and permissions based on job responsibilities and the principle of granting only the minimum access necessary for tasks. Regularly review and update access permissions to reflect organizational changes and limit potential exposure.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Behavior Analytics: Employ advanced monitoring solutions that leverage behavior analytics and machine learning to detect unusual or unauthorized activities in real-time. These tools can identify anomalies in user behavior, system interactions, and data access patterns, alerting security teams to potential threats. Proactive monitoring enhances the ability to respond swiftly and prevent breaches.
- Continuous Employee Training and Awareness: Develop a comprehensive training program for employees that focuses on the importance of data governance, proper cloud usage, and security best practices. Ensure that employees are educated about the risks associated with misconfigurations, credential theft, and vulnerabilities. Regular training refreshes and simulated exercises can help reinforce these principles.
3. Vendor Lock-In
Dropbox’s experience with vendor lock-in illustrates how a heavy reliance on a single cloud provider can limit flexibility. Dropbox initially relied heavily on Amazon Web Services (AWS). As their usage grew, it became increasingly difficult to migrate to other providers due to the tight integration of their applications with AWS services.
- A Flexera report shows that 92% of organizations have a multi-cloud strategy, indicating the recognition of the risks associated with vendor lock-in.
- In the State of the Cloud Report 2021 by Flexera, 80% of respondents reported they have concerns about becoming too dependent on a single cloud provider.
Impact: Vendor lock-in can lead to increased costs and reduced flexibility. As Dropbox struggled to migrate away from AWS, they faced challenges in negotiating competitive pricing with other providers.
Solution:
- Multi-Cloud Strategy Development: Begin by formulating a well-defined multi-cloud strategy that considers the use of multiple cloud providers based on the specific needs of the organization. This strategy should outline the criteria for selecting cloud services, such as performance, features, and pricing, and address potential migration challenges in advance.
- Containerization and Microservices Architecture: Adopt containerization and microservices architecture to increase application portability and reduce dependencies on specific cloud services. Containerization, using tools like Docker and Kubernetes, allows applications to run consistently across different cloud platforms, minimizing the impact of vendor-specific technologies.
- Standardized APIs and Interoperability: Prioritize the use of standardized APIs and interoperable technologies to ensure that applications and data can seamlessly integrate with various cloud providers. By avoiding proprietary APIs and technologies, organizations can prevent deep entanglement with a single vendor’s ecosystem and facilitate easier migration between providers.
- Cloud Agnostic Design Patterns: Implement cloud agnostic design patterns that abstract away vendor-specific details and dependencies. Use design principles that emphasize modularity, scalability, and loose coupling. This approach enables the organization to switch providers or distribute workloads across different clouds with minimal disruption.
- Regular Vendor Review and Negotiations: Continuously evaluate the performance and pricing of cloud providers, even if an organization has already chosen a primary provider. Regular vendor reviews allow the organization to identify potential vendor lock-in risks and negotiate competitive pricing or contractual terms. This approach maintains flexibility and keeps providers accountable.
4. Performance and Latency Issues
Robinhood’s experience highlights the performance challenges associated with cloud infrastructure during periods of high demand. The stock trading platform faced performance issues during times of market volatility. Users encountered delayed order executions and system outages, impacting their ability to trade effectively.
- According to a study by Uptime Institute, cloud-related outages increased by 10% in 2023 compared to the previous year. With more than two-thirds of all outages costing more than $100,000, the business case for investing more in resiliency — and training — is becoming stronger.
- The Report also found that 43% of respondents cited performance as a top cloud challenge, up from 38% in 2022.
Impact: The performance issues resulted in user frustration and negative media coverage. Robinhood’s reputation was tarnished due to their inability to provide a seamless trading experience during critical market conditions. Here are some of the long standing impacts faced by the company – In the first quarter of 2022, Robinhood’s revenue fell by 43% year-over-year. This was largely due to the performance issues, which led to a decrease in trading activity. They also reported a net loss of $413 million in the first quarter of 2022. This was the company’s first quarterly loss since going public in 2021.
The performance issues also led to a decline in Robinhood’s user base. In the first quarter of 2022, the company’s active users fell by 10% year-over-year.
Solution:
- Performance Monitoring and Scalability Planning: Begin by implementing robust performance monitoring tools that provide real-time insights into the health and performance of cloud-based applications and services. Utilize these insights to identify patterns of usage, predict peak demand periods, and plan for scalability accordingly. Proactively allocate resources to handle increased traffic during high-demand periods.
- Load Balancing and Distribution: Implement intelligent load balancing mechanisms that distribute traffic across multiple instances and regions. Load balancing helps prevent overloading of specific resources, reducing the risk of latency and performance degradation. Utilize content delivery networks (CDNs) to cache and serve content from servers located closer to end-users, improving response times.
- Resilience and Redundancy Design: Design applications and services with resilience and redundancy in mind. Implement fault-tolerant architectures that allow for automatic failover and data replication across multiple availability zones or regions. This ensures that even in the event of hardware or network failures, services remain available with minimal disruption.
- Performance Testing and Optimization: Conduct regular performance testing to identify bottlenecks, latency issues, and areas for optimization within the cloud infrastructure. Load testing, stress testing, and capacity planning exercises help simulate real-world scenarios and ensure that the infrastructure can handle peak workloads without compromising performance.
- Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Region Deployment: Consider adopting a hybrid cloud strategy that combines both on-premises and cloud resources, allowing critical workloads to run on-premises during periods of high demand. Additionally, deploy applications across multiple regions of a cloud provider to minimize latency and improve availability for geographically dispersed users.
5. Data Transfer and Migration Challenges
TSB Bank’s migration disaster in 2018 serves as a cautionary tale about the complexities of data migration. The bank attempted to migrate its IT platform, resulting in a catastrophic failure. Customers were locked out of their accounts, transactions failed, and online services were disrupted for an extended period.
- According to Gartner, through 2023, more than 75% of enterprises will experience at least one unsuccessful migration, leading to additional costs and delays.
- The State of the Cloud Report 2023 by Flexera indicates that 49% of enterprises cited migrating applications as the top cloud challenge, highlighting the complexity of migrations.
Impact: The migration debacle led to substantial financial losses, regulatory investigations, and severe reputational damage. The bank has estimated that the total cost of the incident was £200 million, including: £32.7 million in compensation to customers who were affected, £318 million in costs associated with the migration itself, such as IT consultants and contractors, £107.4 million in lost revenue, as customers were unable to access their accounts or make payments during the disruption and a fine £48.6 million by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) for its failings in relation to the migration. Moreover, the bank’s share price fell by 10% in the days following the incident.
Solution
- Thorough Planning and Assessment: Begin with a comprehensive planning phase that involves a detailed assessment of the existing IT environment, data dependencies, and application interdependencies. Identify potential roadblocks and challenges that might arise during migration. Develop a clear migration strategy that includes a phased approach, prioritizing critical applications and data for a smooth transition.
- Pilot Testing and Validation: Before embarking on a full-scale migration, conduct pilot tests to validate the migration process. Choose non-critical applications or workloads to test the migration process, data integrity, and performance. Pilot tests help identify any unforeseen issues and allow for adjustments before migrating mission-critical data and applications.
- Data Cleansing and Transformation: Invest time in data cleansing, transformation, and consolidation efforts before migration. Eliminate duplicate, obsolete, or irrelevant data to ensure a streamlined migration process. Convert data formats if necessary, ensuring compatibility with the target cloud environment and applications.
- Incremental Migration with Rollback Plans: Implement an incremental migration approach where data and applications are migrated in stages. This strategy minimizes the impact of potential failures and allows for easy rollback in case of issues. Each phase of migration should be thoroughly tested and validated before proceeding to the next.
- Collaboration and Expert Support: Engage with cloud migration experts, consultants, and your cloud service provider to ensure a successful migration. Collaborate closely with technical teams, business stakeholders, and end-users to gather insights and address concerns. Expert guidance can help navigate complexities and mitigate risks during the migration process.
Each of these real-world examples casts a spotlight on the gripping challenges that financial institutions grapple with when embarking on the journey of cloud migration. Security breaches, data governance lapses, vendor lock-in issues, performance hiccups, and migration failures – all stand as stark reminders of the high-stakes nature of this transformation. Yet, amidst these trials lies an opportunity. By fortifying their defenses with robust security measures, deploying effective data governance strategies, embracing multi-cloud approaches, harnessing performance optimization tactics, and meticulously planning ahead of migrations, banks can navigate these challenges. In doing so, they not only safeguard their operations and customers but also secure their financial well-being in the boundless skies of the cloud.
Microsoft Azure: Your Partner of Choice
Microsoft Azure offers a suite of tools and services that specifically assist the finance sector in facilitating intelligent migration to the cloud. These tools cater to various aspects of the migration process, ensuring security, compliance, data management, and operational efficiency. Here are some of the key tools provided by Azure for intelligent cloud migration in the finance industry:
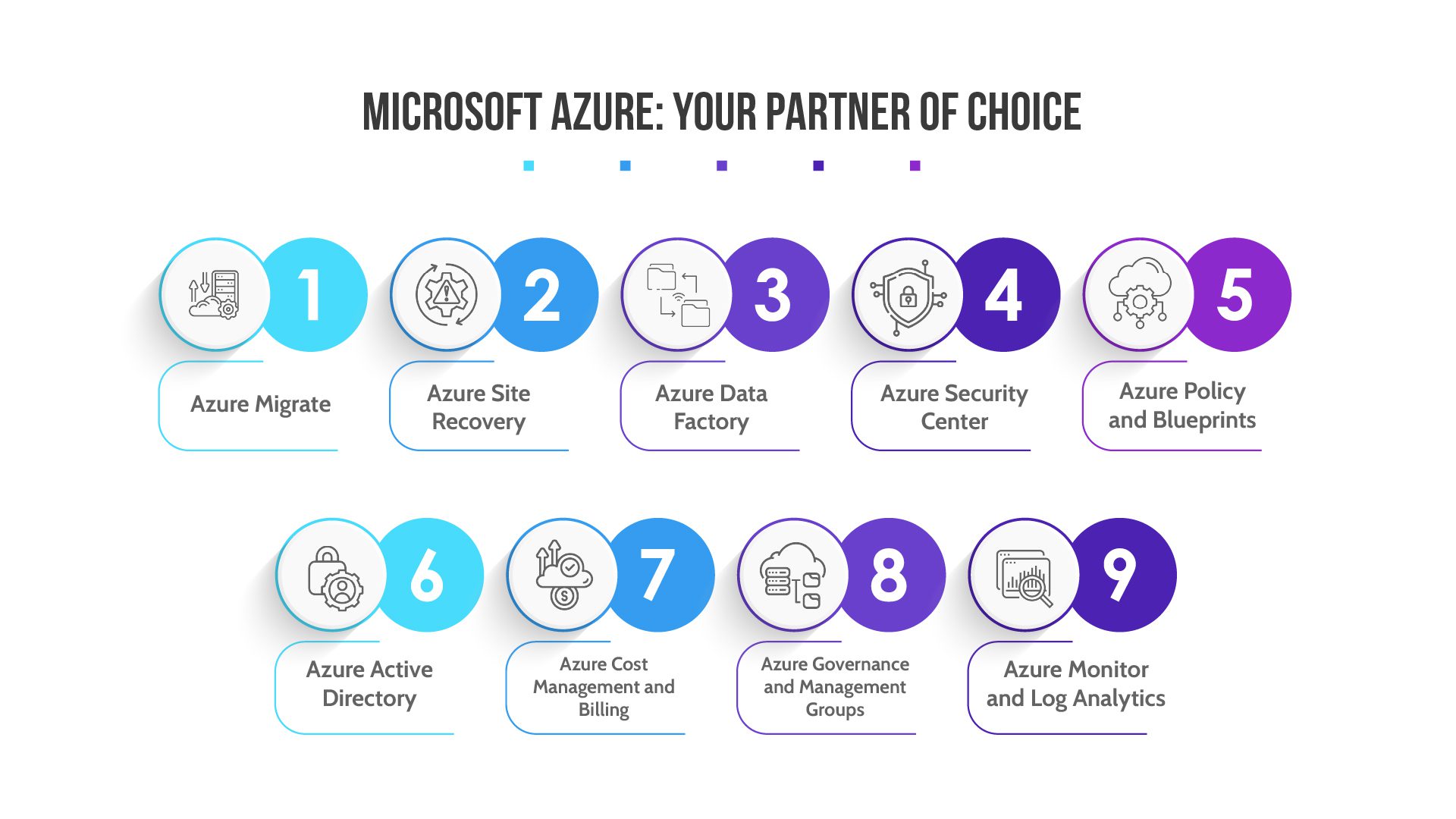
- Azure Migrate: Azure Migrate is a centralized hub that assists in planning, assessing, and executing migration projects. It provides discovery and assessment of on-premises workloads, enabling financial institutions to determine the readiness of applications for migration to Azure. This tool helps in right-sizing resources and estimating costs, aiding in a seamless transition.
- Azure Site Recovery: This tool is critical for disaster recovery and business continuity. It enables the replication of on-premises applications and data to Azure, ensuring data availability in case of disruptions. For the finance sector, where uptime and data integrity are paramount, Azure Site Recovery plays a significant role in maintaining operational resilience.
- Azure Data Factory: Azure Data Factory simplifies the process of moving data from various sources to Azure. For financial institutions, this tool helps ensure that sensitive financial data is securely and efficiently migrated to the cloud while maintaining data quality and integrity.
- Azure Security Center: Security is a top concern in the finance sector. Azure Security Center provides advanced threat protection and security management for Azure resources. It identifies and helps address potential security vulnerabilities during migration and ongoing operations, safeguarding against cyber threats.
- Azure Policy and Blueprints: Azure Policy enables financial institutions to enforce organizational standards and compliance by defining and enforcing rules and guidelines for cloud resources. Azure Blueprints allows creating reusable deployment templates, ensuring consistency and compliance across the organization’s cloud environment.
- Azure Active Directory: For identity and access management, Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) ensures secure authentication and access control to cloud resources. It’s crucial for maintaining strict control over who can access sensitive financial data and services.
- Azure Cost Management and Billing: Financial institutions need to manage their cloud spending effectively. Azure Cost Management and Billing provides visibility into cloud costs, helps optimize spending, and ensures adherence to budgetary constraints.
- Azure Governance and Management Groups: These tools allow organizations to manage and organize Azure resources in a hierarchical structure. For financial institutions with complex infrastructure, these tools provide efficient resource organization and management.
- Azure Monitor and Log Analytics: Azure Monitor provides comprehensive monitoring of applications and infrastructure, while Log Analytics offers advanced analytics and insights into data generated by cloud resources. These tools assist financial institutions in ensuring the availability, performance, and security of their cloud environments.
Harnessing the power of these cutting-edge tools, financial institutions can embark on a cloud migration journey with finesse, tailoring their approach to the unique demands of their enterprise. With a laser focus on security, compliance, data mastery, and resource optimization, these Azure tools act as the compass guiding the finance industry through a transformative cloud experience. The result? A harmonious and safeguarded shift to the cloud that not only upholds operational brilliance but also paints a new landscape of possibilities.
The Data Dynamics Advantage
In line with the mission of facilitating intelligent data migration to the cloud, Microsoft has collaborated with Data Dynamics to introduce the Azure File Migration Program, revolutionizing the way enterprises transition their data to Azure. This strategic partnership presents a groundbreaking opportunity for banks and financial institutions to seamlessly move their unstructured files and object storage data to Azure without any cost-related concerns. With this automated migration process, financial institutions can mitigate risks while upholding control over access and file security, thereby preserving the sanctity of their data. And guess what!!! The migrations are FREE. Click to know more.
Also, this collaboration between Microsoft and Data Dynamics extends beyond data migration, aiming to invigorate intelligent data management across various environments, including On-Premise, Azure, and Hybrid Cloud. By participating in the program, financial institutions gain the advantage of enrolling in migration projects facilitated by Data Dynamics, facilitating a seamless transition to the Azure platform.
The distinctive attributes of Data Dynamics’ platform set it apart. It provides a spectrum of features designed to facilitate intelligent data tiering to Azure. Through automated migration methods, financial institutions can migrate individual files, folders, shares, or even entire volumes from their on-premises storage to Azure. Employing policy-based data tiering, institutions can establish rules that automatically relocate data to different storage tiers based on its usage patterns. This optimization ensures reduced costs and optimal data placement within the appropriate tier. Data governance, a pivotal concern for the finance sector, is equally addressed by Data Dynamics. The platform enables the implementation of policies that enforce data security measures, including encryption, before storing data in Azure—ensuring full compliance with stringent regulatory requirements.
The Azure File Migration Program, a result of the collaboration between Microsoft and Data Dynamics, directly confronts the formidable challenges encountered during the intricate cloud migration journey. It tackles issues ranging from cost efficiency and data speed to talent acquisition and risk management. By embracing this program, banks and financial institutions can confidently navigate the intricate nuances of cloud computing, unlocking its transformative potential.
To delve deeper into the capabilities of Data Dynamics and the manner in which our platform seamlessly facilitates zero-cost data migration, efficient data management, and cost optimization within Azure, we invite you to explore our website at www.datadynamicsinc.com/microsoft/ . For inquiries, you can reach out to us at solutions@datdyn.com or connect via phone at (713)-491-4298 or +44-(20)-45520800. Allow us to serve as your trusted partner in your journey toward cloud migration and meticulous data management within the finance sector.






